Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma
KEYTRUDA, in combination with LENVIMA, is indicated for the first-line treatment of adult patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC).

IO = immunotherapy; TKI = tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Clear Cell RCC
Studied in the first-line setting across MSKCC risk groups
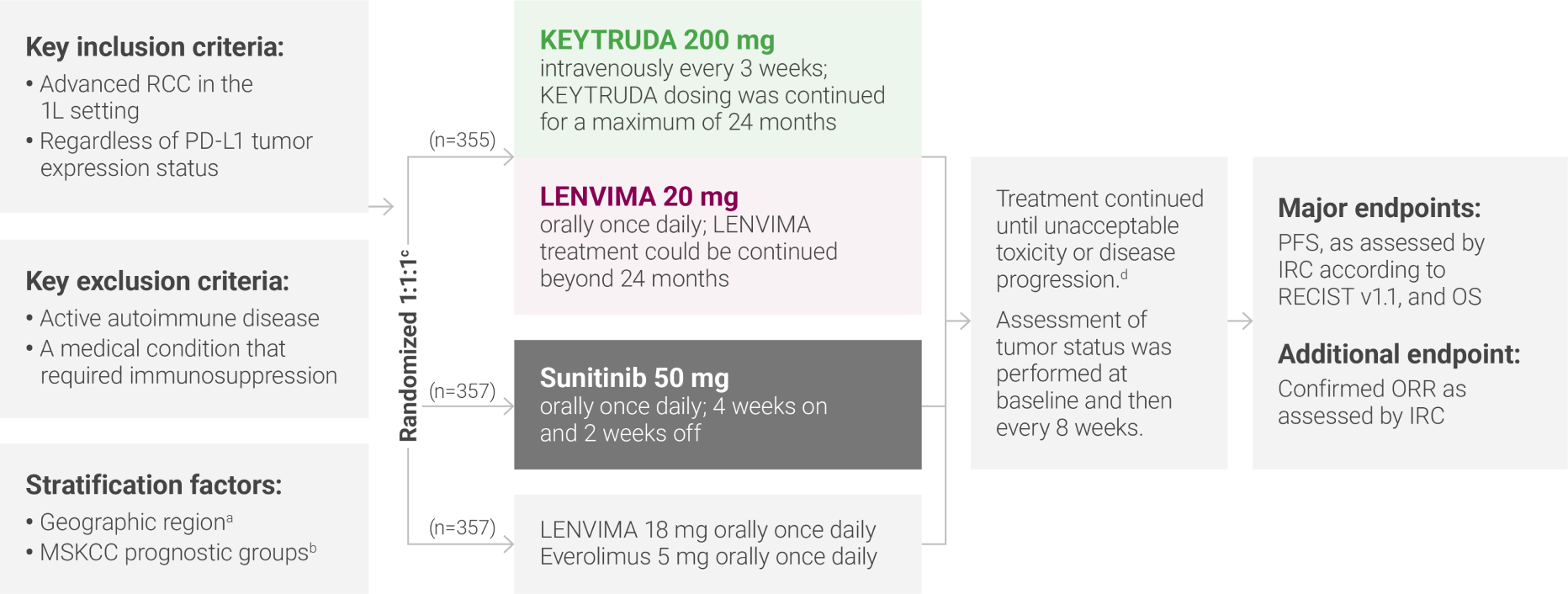
aNorth America and Western Europe vs “Rest of the World.”
bRandomization was stratified according to Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) prognostic risk groups: favorable vs intermediate vs poor.
cClinical data are presented from the KEYTRUDA + LENVIMA and sunitinib arms.
dAdministration of KEYTRUDA with LENVIMA was permitted beyond RECIST-defined disease progression, if the patient was clinically stable and considered by the investigator to be deriving clinical benefit.
1L = first-line; IRC = independent radiologic review committee; ORR = objective response rate; OS = overall survival; PD-L1 = programmed death ligand 1; PFS = progression-free survival; RECIST v1.1 = Response Evaluation Criteria In Solid Tumors v1.1.

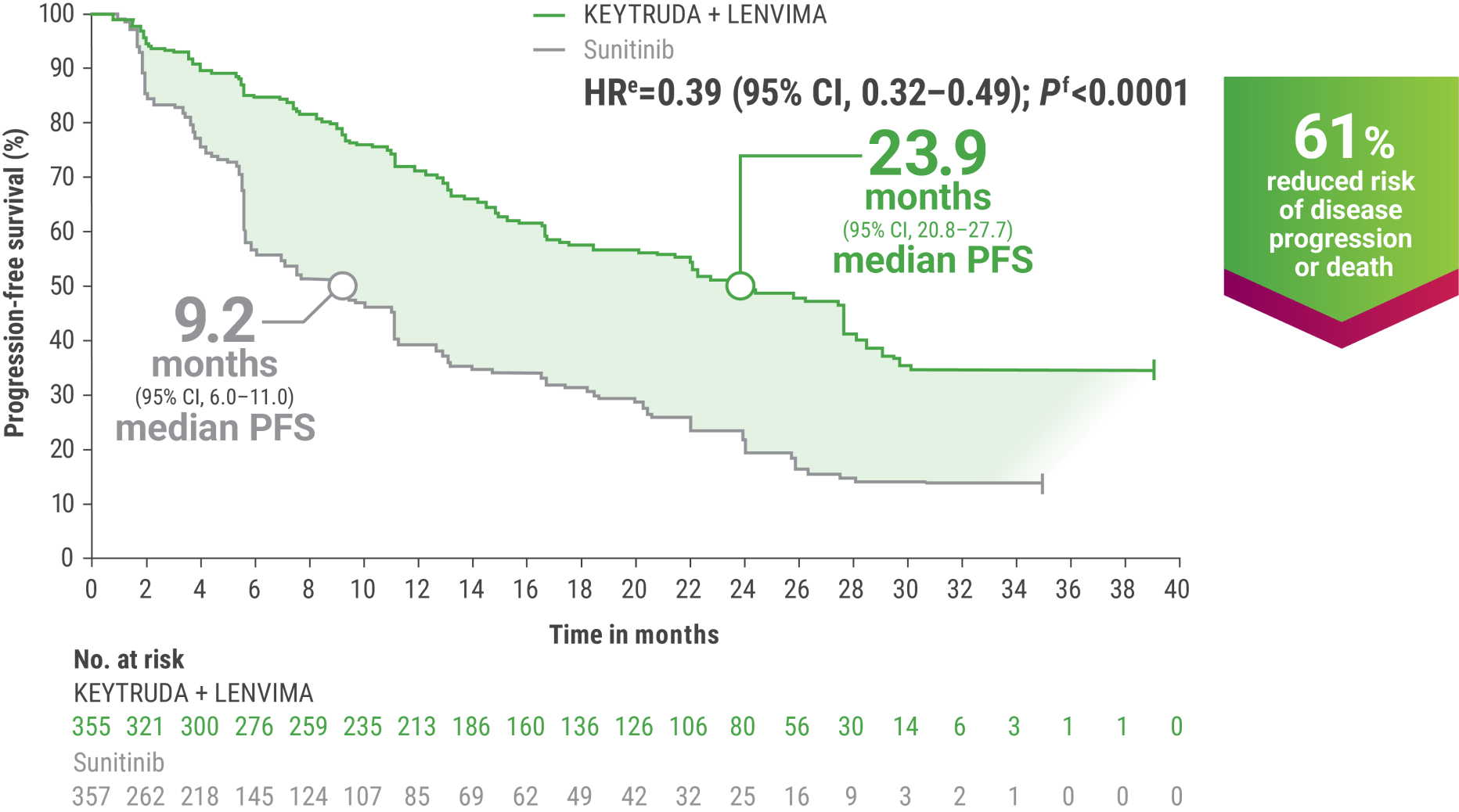

eHazard ratio is based on a Cox Proportional Hazards Model. Stratified by geographic region and MSKCC prognostic groups.
fTwo-sided P value based on stratified log-rank test.
gTumor assessments were based on RECIST v1.1; data cutoff date = 28 Aug 2020.

OS and PFS were major endpoints in the KEYNOTE-581/CLEAR trial.
eHazard ratio is based on a Cox Proportional Hazards Model. Stratified by geographic region and MSKCC prognostic groups.
fTwo-sided P value based on stratified log-rank test.
hData cutoff date = 28 Aug 2020.
This protocol-specified final analysis occurred after the interim analysis, which demonstrated the superiority of OS with KEYTRUDA + LENVIMA vs sunitinib. No statistical testing was planned for the protocol-specified final OS analysis.
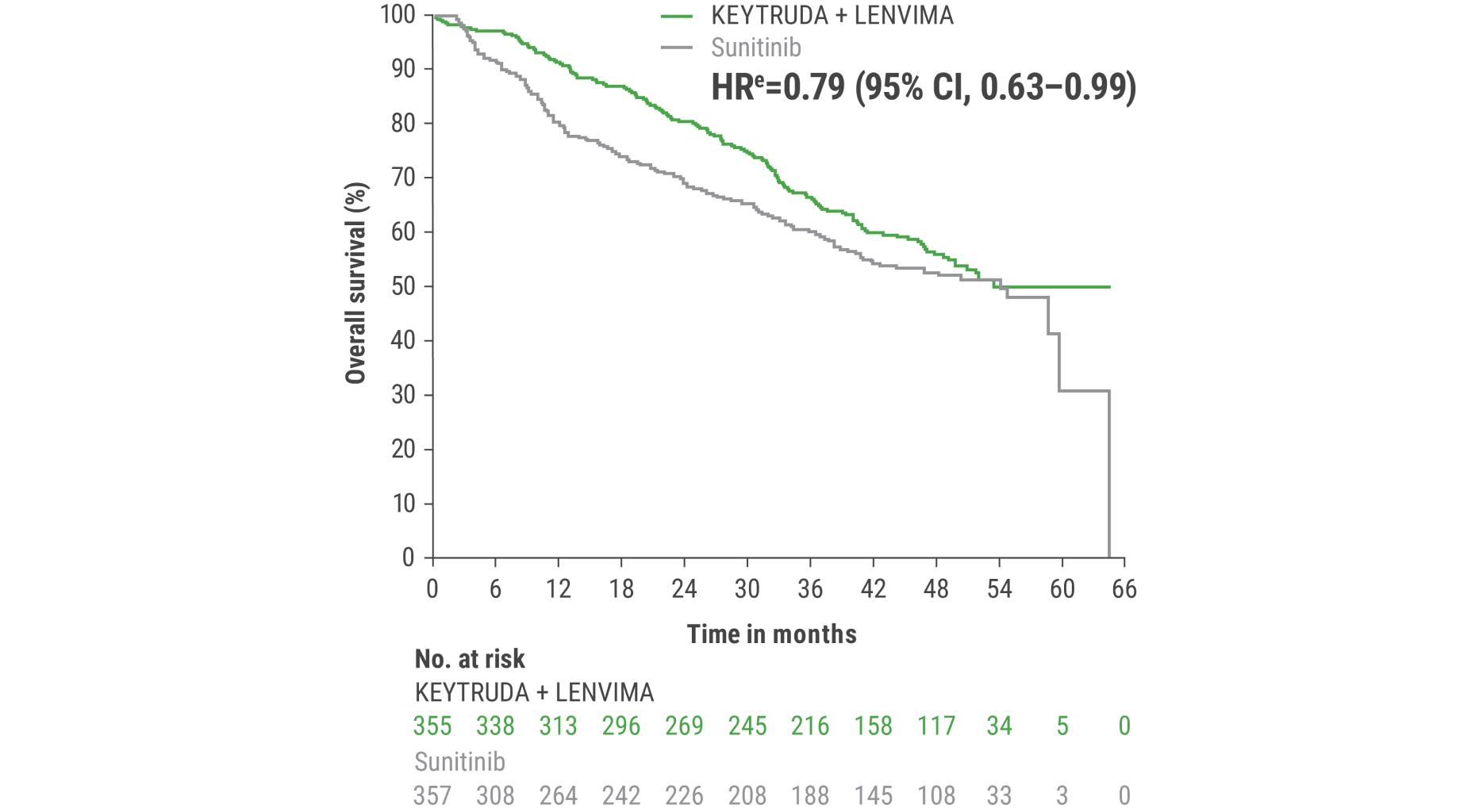
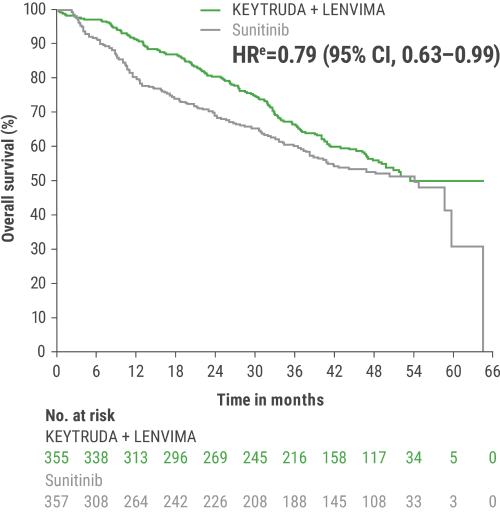
eHazard ratio is based on a Cox Proportional Hazards Model. Stratified by geographic region and MSKCC prognostic groups.
iAn updated OS analysis was conducted when 304 deaths were observed based on the planned number of deaths for the prespecified final analysis.
jUpdated OS cutoff date = 31 July 2022.
CR was 16% with KEYTRUDA + LENVIMA vs 4% with sunitinib.
PR was 55% with KEYTRUDA + LENVIMA vs 32% with sunitinib.
ORR was an additional endpoint in the KEYNOTE-581/CLEAR trial.
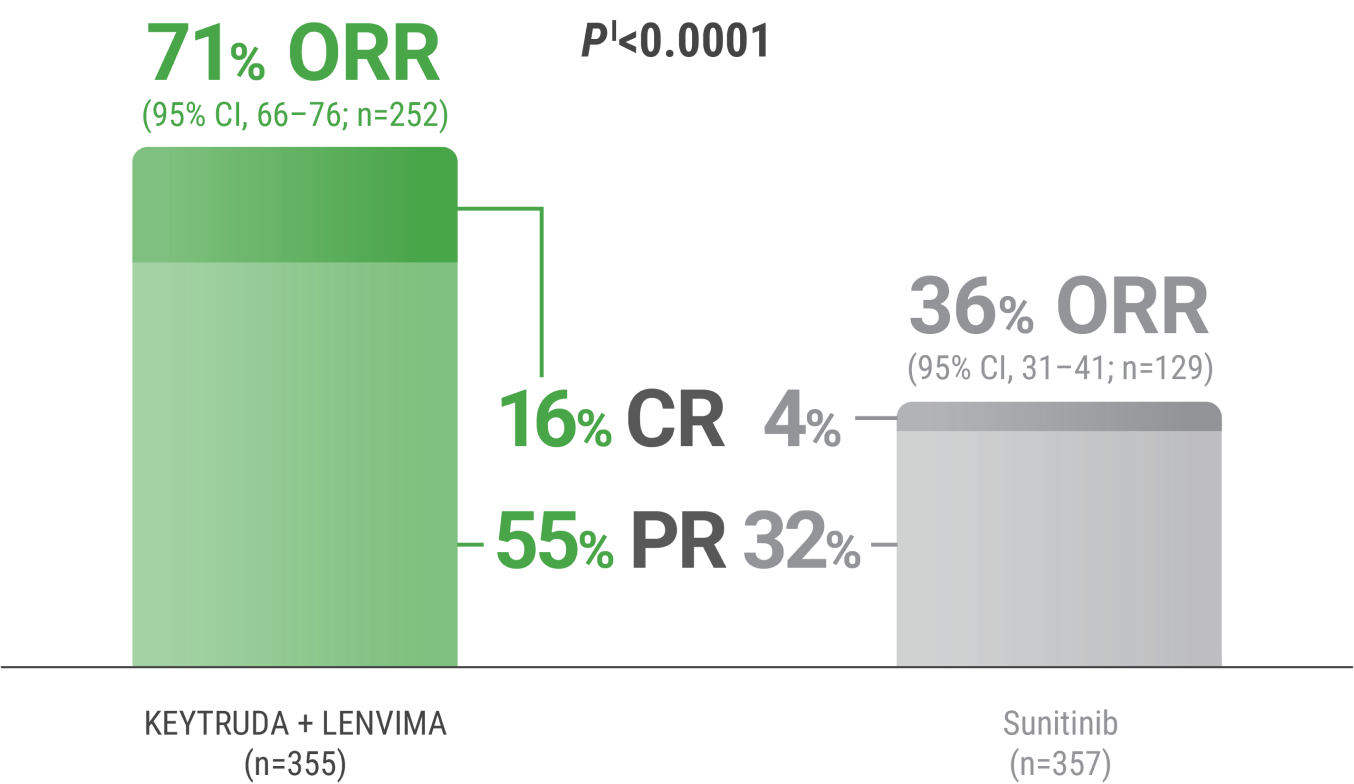
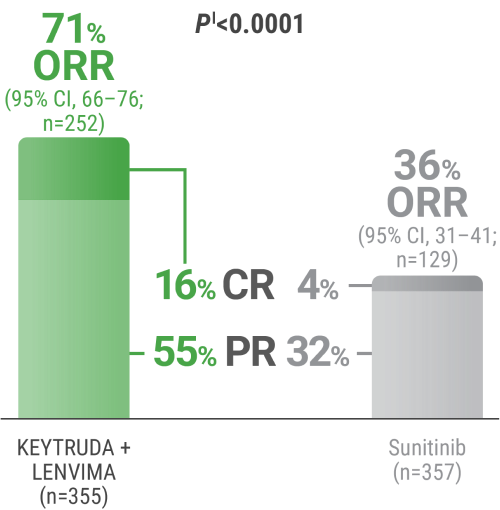
kTumor assessments were based on RECIST v1.1; only confirmed responses are included for ORR. Data cutoff date = 28 Aug 2020.
lTwo-sided P value based upon CMH test.
CR = complete response; PR = partial response; CMH = Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel.
NON-Clear Cell RCC

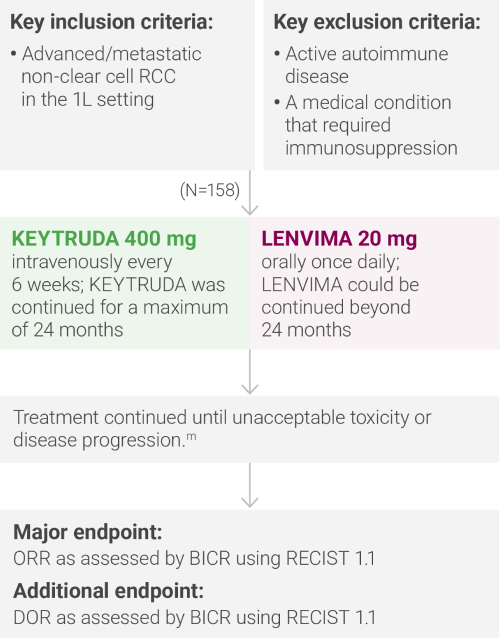
mAdministration of KEYTRUDA with LENVIMA was permitted beyond RECIST-defined disease progression if the patient was considered by the investigator to be deriving clinical benefit.
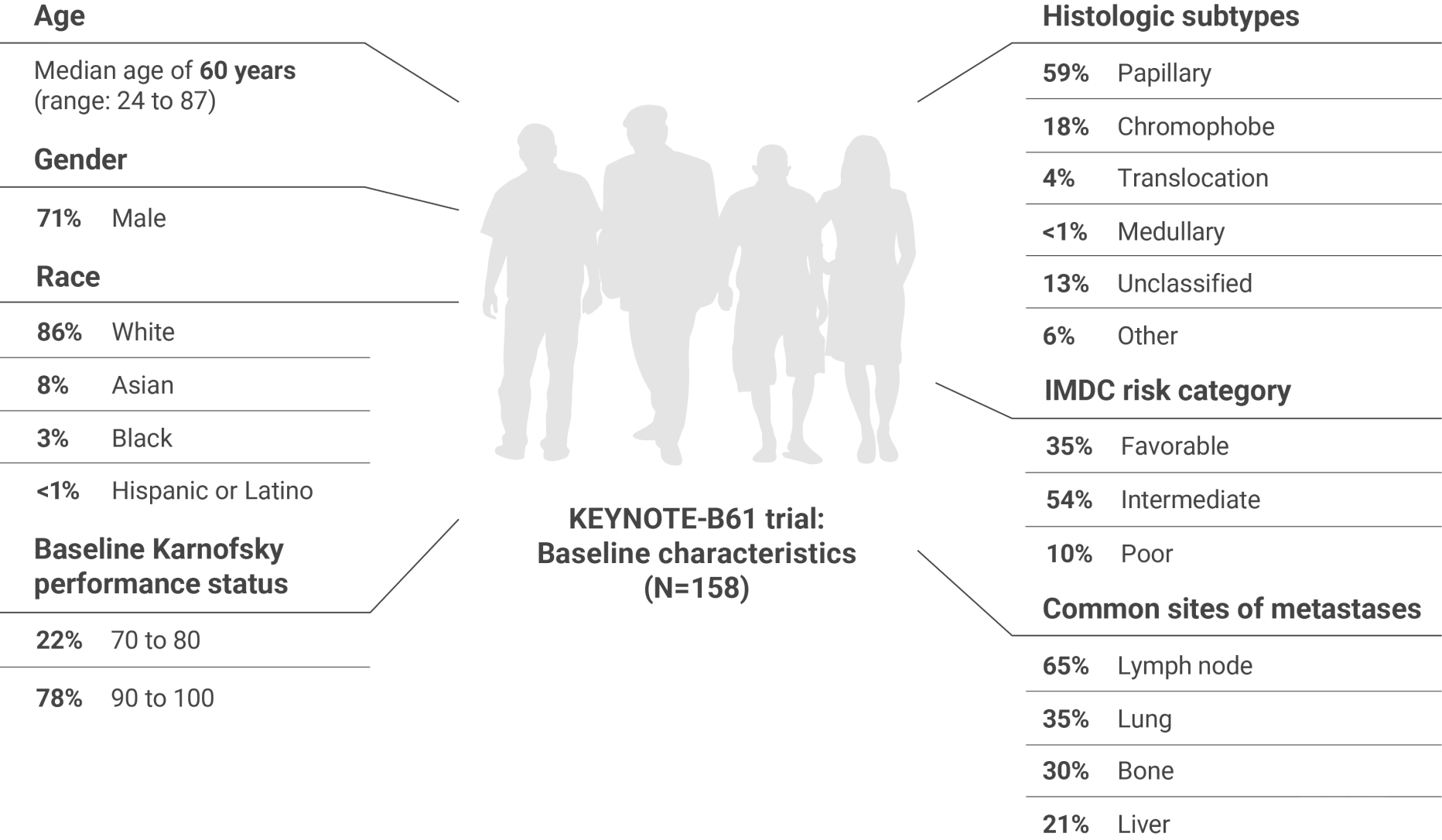
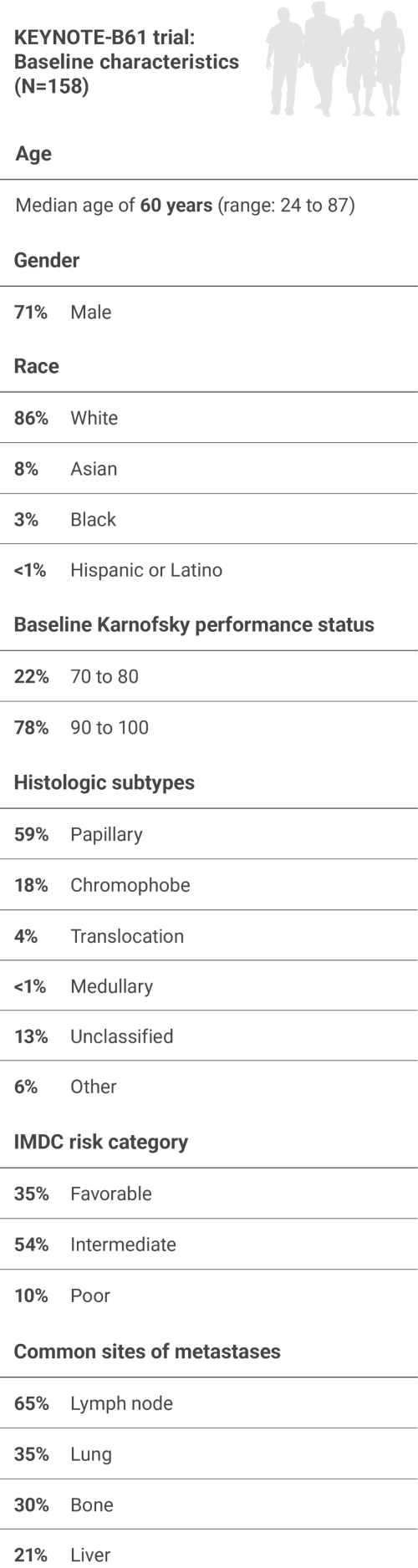
IMDC = International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium; BICR = blinded independent central review; RECIST 1.1 = Response Evaluation Criteria In Solid Tumors 1.1; DOR = duration of response.
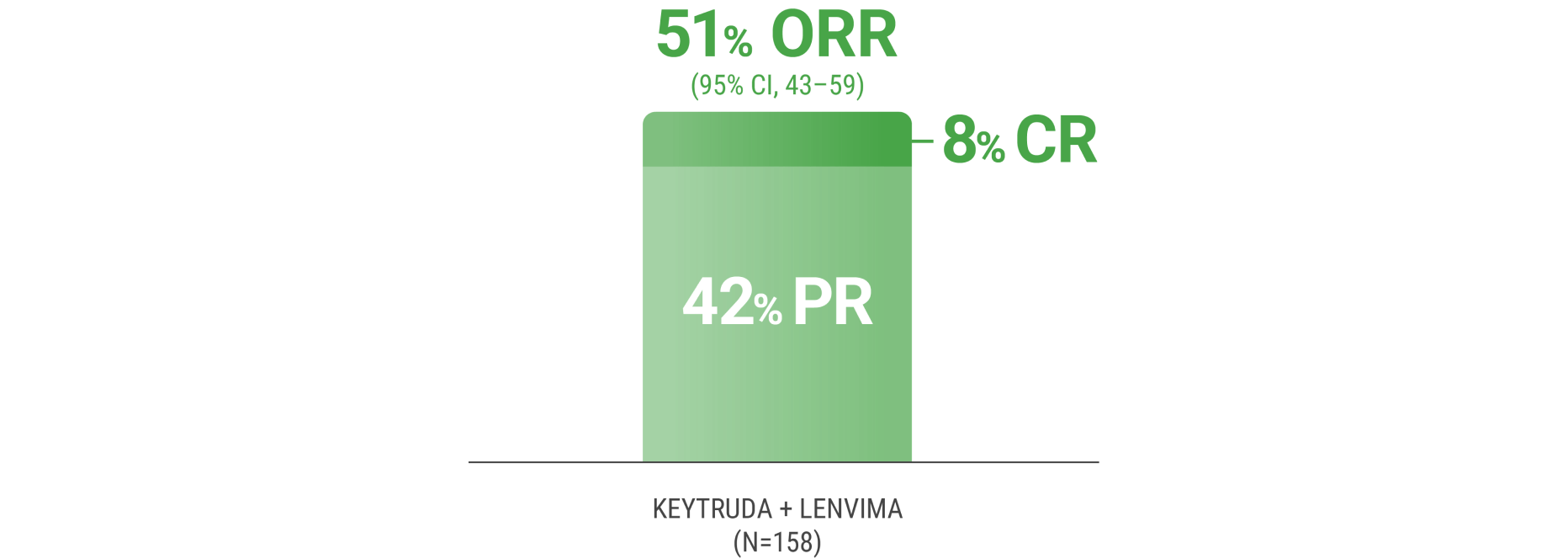
ORR was the major endpoint in the KEYNOTE-B61 trial.
ORRn: 51% (95% CI, 43–59) with KEYTRUDA + LENVIMA.
CR: 8% with KEYTRUDA + LENVIMA.
PR: 42% with KEYTRUDA + LENVIMA.
The sum of PR and CR percentages do not equal that of ORR due to rounding.
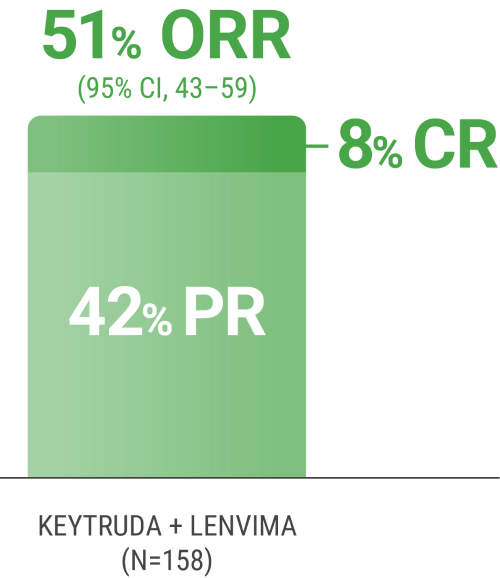
nORR was assessed by BICR using RECIST 1.1.
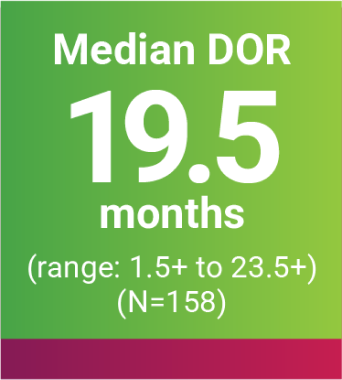
DOR was an additional endpoint in the KEYNOTE-B61 trial.
oBased on Kaplan-Meier estimates.
p“+” denotes ongoing response.
Adverse Reactions
The safety of KEYTRUDA + LENVIMA was investigated in the KEYNOTE-581/CLEAR trial in patients treated with KEYTRUDA + LENVIMA (n=352) compared to sunitinib (n=340) at the protocol-specified interim analysis.
Arrhythmia
Autoimmune hepatitis
Dyspnea
Hypertensive crisis
Increased blood creatinine
Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome
Myasthenic syndrome
Myocarditis
Nephritis
Pneumonitis
Ruptured aneurysm
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 51% of patients receiving
Hemorrhagic events (5%)
Diarrhea (4%)
Hypertension (3%)
Myocardial infarction (3%)
Pneumonitis (3%)
Vomiting (3%)
Acute kidney injury (2%)
Adrenal insufficiency (2%)
Dyspnea (2%)
Pneumonia (2%)
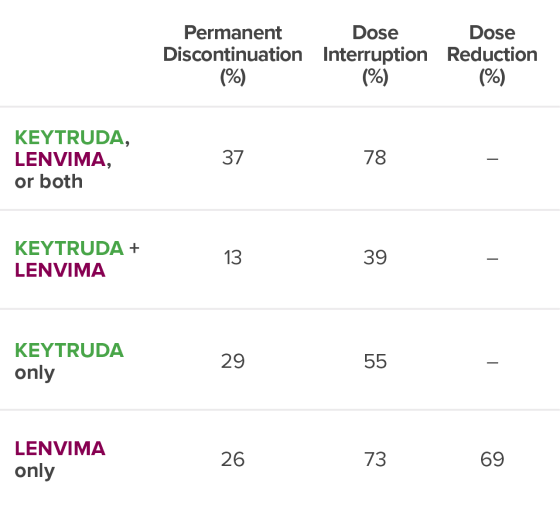
Permanent Discontinuation (%)
Dose
Interruption (%)
Dose Reduction (%)
37
78
–
13
39
–
29
55
–
26
73
69
No dose reduction for
No dose reduction for
Pneumonitis (3%)
Myocardial infarction (3%)
Hepatotoxicity (3%)
Acute kidney injury (3%)
Rash (3%)
Diarrhea (2%)
Diarrhea (10%)
Hepatotoxicity (8%)
Fatigue (7%)
Lipase increased (5%)
Amylase increased (4%)
Musculoskeletal pain (3%)
Hypertension (3%)
Rash (3%)
Acute kidney injury (3%)
Decreased appetite (3%)
Diarrhea (26%)
Fatigue (18%)
Hypertension (17%)
Proteinuria (13%)
Decreased appetite (12%)
Palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia (11%)
Nausea (9%)
Stomatitis (9%)
Musculoskeletal pain (8%)
Rash (8%)
Increased lipase (7%)
Abdominal pain (6%)
Vomiting (6%)
Increased ALT (5%)
Increased amylase (5%)
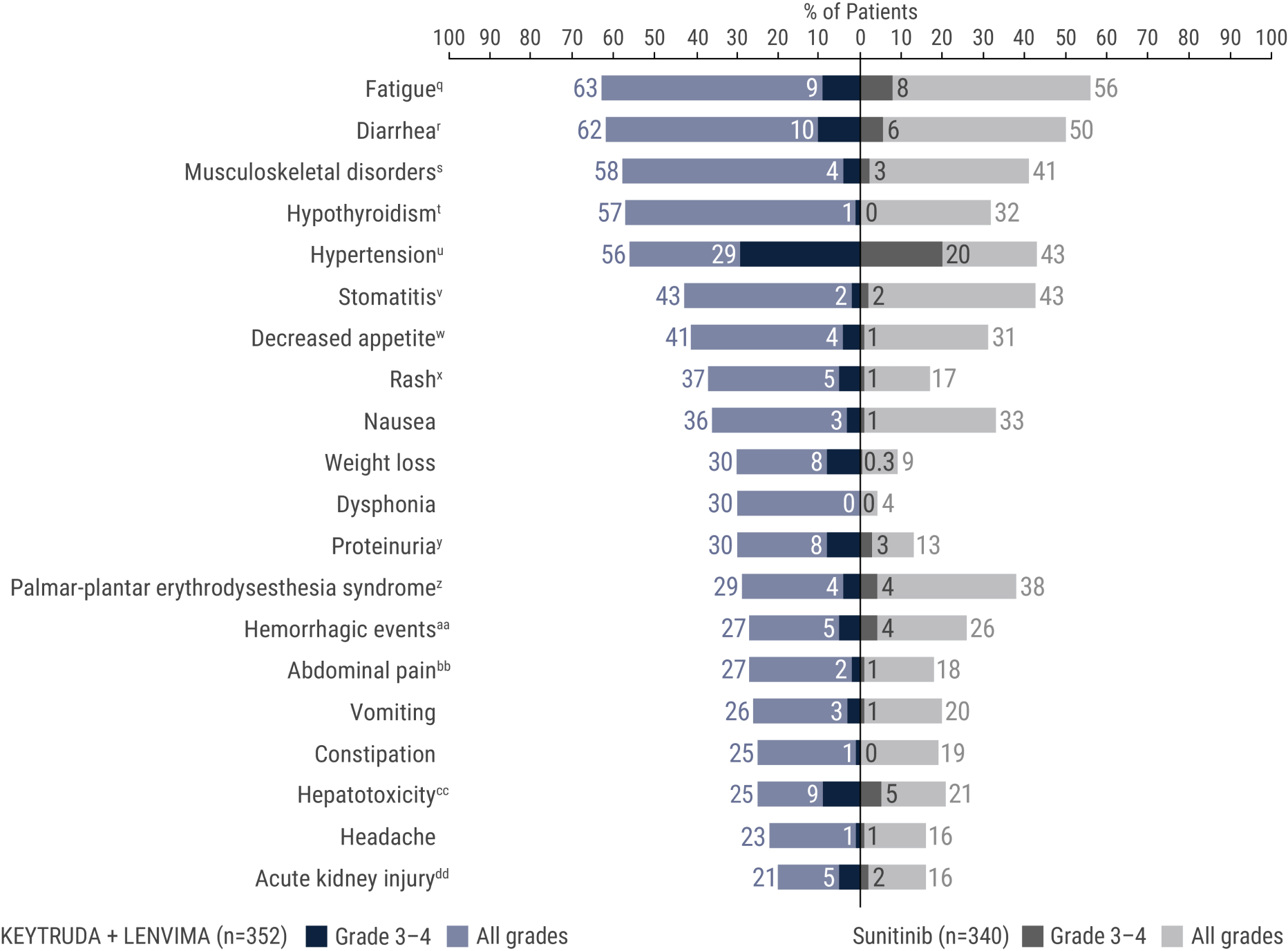
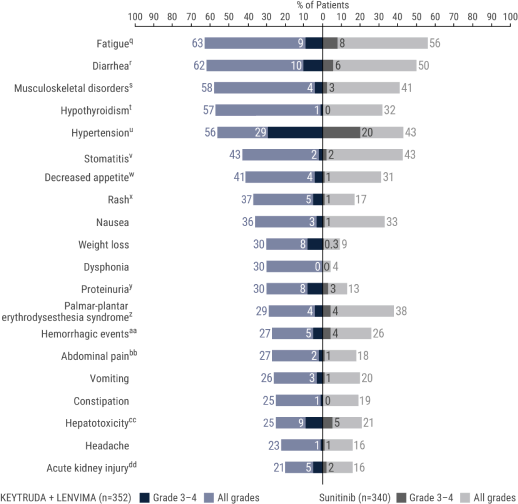
qIncludes asthenia, fatigue, lethargy, malaise.
rIncludes diarrhea, gastroenteritis.
sIncludes arthralgia, arthritis, back pain, bone pain, breast pain, musculoskeletal chest pain, musculoskeletal discomfort, musculoskeletal pain, musculoskeletal stiffness, myalgia, neck pain, non-cardiac chest pain, pain in extremity, pain in jaw.
tIncludes hypothyroidism, increased blood thyroid stimulating hormone, secondary hypothyroidism.
uIncludes essential hypertension, increased blood pressure, increased diastolic blood pressure, hypertension, hypertensive crisis, hypertensive retinopathy, labile blood pressure.
vIncludes aphthous ulcer, gingival pain, glossitis, glossodynia, mouth ulceration, mucosal inflammation, oral discomfort, oral mucosal blistering, oral pain, oropharyngeal pain, pharyngeal inflammation, stomatitis.
wIncludes decreased appetite, early satiety.
xIncludes genital rash, infusion site rash, penile rash, perineal rash, rash, rash erythematous, rash macular, rash maculo-papular, rash papular, rash pruritic, rash pustular.
yIncludes hemoglobinuria, nephrotic syndrome, proteinuria.
zIncludes palmar erythema, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome, plantar erythema.
aaIncludes all hemorrhage terms. Hemorrhage terms that occurred in 1 or more subjects in either treatment group include anal hemorrhage, aneurysm ruptured, blood blister, blood loss anemia, blood urine present, catheter site hematoma, cerebral microhemorrhage, conjunctival hemorrhage, contusion, diarrhea hemorrhagic, disseminated intravascular coagulation, ecchymosis, epistaxis, eye hemorrhage, gastric hemorrhage, gastritis hemorrhagic, gingival bleeding, hemorrhage urinary tract, hemothorax, hematemesis, hematoma, hematochezia, hematuria, hemoptysis, hemorrhoidal hemorrhage, increased tendency to bruise, injection site hematoma, injection site hemorrhage, intra-abdominal hemorrhage, lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage, Mallory-Weiss syndrome, melaena, petechiae, rectal hemorrhage, renal hemorrhage, retroperitoneal hemorrhage, small intestinal hemorrhage, splinter hemorrhages, subcutaneous hematoma, subdural hematoma, subarachnoid hemorrhage, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, tumor hemorrhage, traumatic hematoma, upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage.
bbIncludes abdominal discomfort, abdominal pain, abdominal rigidity, abdominal tenderness, epigastric discomfort, lower abdominal pain, upper abdominal pain.
ccIncludes alanine aminotransferase increased, aspartate aminotransferase increased, blood bilirubin increased, drug-induced liver injury, hepatic enzyme increased, hepatic failure, hepatic function abnormal, hepatocellular injury, hepatotoxicity, hyperbilirubinemia, hypertransaminasemia, immune-mediated hepatitis, liver function test increased, liver injury, transaminases increased, gamma-glutamyltransferase increased.
ddIncludes acute kidney injury, azotemia, blood creatinine increased, creatinine renal clearance decreased, hypercreatininemia, renal failure, renal impairment, oliguria, glomerular filtration rate decreased, nephropathy toxic.
NCCN RECOMMENDATIONS
NCCN recommends pembrolizumab (
Favorable
Intermediate
Poor
CATEGORY 1
PREFERRED
CATEGORY 1
PREFERRED
CATEGORY 1
PREFERRED
Favorable
CATEGORY 1
PREFERRED
Intermediate
CATEGORY 1
PREFERRED
Poor
CATEGORY 1
PREFERRED
NCCN makes no warranties of any kind whatsoever regarding their content, use, or application and disclaims any responsibility for their application or use in any way.
Category 1: Based upon high-level evidence (≥1 randomized phase 3 trials or high-quality, robust meta-analyses), there is uniform NCCN consensus (≥85% support of the Panel) that the intervention is appropriate.11
Category 2A: Based upon lower-level evidence, there is uniform NCCN consensus (≥85% support of the Panel) that the intervention is appropriate.11
IMDC = International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium; MSKCC = Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center.
Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma
KEYTRUDA, in combination with LENVIMA, is indicated for the first-line treatment of adult patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
Advanced Endometrial Carcinoma
KEYTRUDA, in combination with LENVIMA, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with advanced endometrial carcinoma that is mismatch repair proficient (pMMR) as determined by an FDA-approved test or not microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H), who have disease progression following prior systemic therapy in any setting and are not candidates for curative surgery or radiation.
Severe and Fatal Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions
Immune-Mediated Pneumonitis
Immune-Mediated Colitis
Hepatotoxicity and Immune-Mediated Hepatitis
KEYTRUDA as a Single Agent
Immune-Mediated Endocrinopathies
Adrenal Insufficiency
Hypophysitis
Thyroid Disorders
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (DM), Which Can Present With Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Immune-Mediated Nephritis With Renal Dysfunction
Immune-Mediated Dermatologic Adverse Reactions
Other Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions
Infusion-Related Reactions
Complications of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (HSCT)
Increased Mortality in Patients With Multiple Myeloma
Embryofetal Toxicity
Adverse Reactions
Lactation
Hypertension
Cardiac Dysfunction
Arterial Thromboembolic Events
Hepatotoxicity
Renal Failure or Impairment
Proteinuria
Diarrhea
Fistula Formation and Gastrointestinal Perforation
QT Interval Prolongation
Hypocalcemia
Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome (RPLS)
Hemorrhagic Events
Impairment of Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Suppression/Thyroid Dysfunction
Impaired Wound Healing
Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (ONJ)
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Adverse Reactions
Use in Specific Populations
KEYTRUDA, in combination with LENVIMA, is indicated for the first-line treatment of adult patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
KEYTRUDA, in combination with LENVIMA, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with advanced endometrial carcinoma that is mismatch repair proficient (pMMR) as determined by an FDA-approved test or not microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H), who have disease progression following prior systemic therapy in any setting and are not candidates for curative surgery or radiation.
Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma
KEYTRUDA, in combination with LENVIMA, is indicated for the first-line treatment of adult patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
Advanced Endometrial Carcinoma
KEYTRUDA, in combination with LENVIMA, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with advanced endometrial carcinoma that is mismatch repair proficient (pMMR) as determined by an FDA-approved test or not microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H), who have disease progression following prior systemic therapy in any setting and are not candidates for curative surgery or radiation.
Severe and Fatal Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions: KEYTRUDA is a monoclonal antibody that belongs to a class of drugs that bind to either the programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1) or the programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1), blocking the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway, thereby removing inhibition of the immune response, potentially breaking peripheral tolerance and inducing immune-mediated adverse reactions. Immune-mediated adverse reactions, which may be severe or fatal, can occur in any organ system or tissue, can affect more than one body system simultaneously, and can occur at any time after starting treatment or after discontinuation of treatment. Important immune-mediated adverse reactions listed here may not include all possible severe and fatal immune-mediated adverse reactions.
Hypertension: In differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC), hypertension occurred in 73% of patients on LENVIMA (44% grade 3-4). In advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC), hypertension occurred in 42% of patients on LENVIMA + everolimus (13% grade 3). Systolic blood pressure ≥160 mmHg occurred in 29% of patients, and 21% had diastolic blood pressure ≥100 mmHg. In unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), hypertension occurred in 45% of LENVIMA-treated patients (24% grade 3). Grade 4 hypertension was not reported in HCC.
Severe and Fatal Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions
Immune-Mediated Pneumonitis
Immune-Mediated Colitis
Hepatotoxicity and Immune-Mediated Hepatitis
KEYTRUDA as a Single Agent
Immune-Mediated Endocrinopathies
Adrenal Insufficiency
Hypophysitis
Thyroid Disorders
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (DM), Which Can Present With Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Immune-Mediated Nephritis With Renal Dysfunction
Immune-Mediated Dermatologic Adverse Reactions
Other Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions
Infusion-Related Reactions
Complications of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (HSCT)
Increased Mortality in Patients With Multiple Myeloma
Embryofetal Toxicity
Adverse Reactions
Lactation
Hypertension
Cardiac Dysfunction
Arterial Thromboembolic Events
Hepatotoxicity
Renal Failure or Impairment
Proteinuria
Diarrhea
Fistula Formation and Gastrointestinal Perforation
QT Interval Prolongation
Hypocalcemia
Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome (RPLS)
Hemorrhagic Events
Impairment of Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Suppression/Thyroid Dysfunction
Impaired Wound Healing
Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (ONJ)
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Adverse Reactions
Use in Specific Populations
Severe and Fatal Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions: KEYTRUDA is a monoclonal antibody that belongs to a class of drugs that bind to either the programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1) or the programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1), blocking the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway, thereby removing inhibition of the immune response, potentially breaking peripheral tolerance and inducing immune-mediated adverse reactions. Immune-mediated adverse reactions, which may be severe or fatal, can occur in any organ system or tissue, can affect more than one body system simultaneously, and can occur at any time after starting treatment or after discontinuation of treatment. Important immune-mediated adverse reactions listed here may not include all possible severe and fatal immune-mediated adverse reactions.
Severe and Fatal Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions
Immune-Mediated Pneumonitis
Immune-Mediated Colitis
Hepatotoxicity and Immune-Mediated Hepatitis
KEYTRUDA as a Single Agent
Immune-Mediated Endocrinopathies
Adrenal Insufficiency
Hypophysitis
Thyroid Disorders
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (DM), Which Can Present With Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Immune-Mediated Nephritis With Renal Dysfunction
Immune-Mediated Dermatologic Adverse Reactions
Other Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions
Infusion-Related Reactions
Complications of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (HSCT)
Increased Mortality in Patients With Multiple Myeloma
Embryofetal Toxicity
Adverse Reactions
Lactation
Hypertension: In differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC), hypertension occurred in 73% of patients on LENVIMA (44% grade 3-4). In advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC), hypertension occurred in 42% of patients on LENVIMA + everolimus (13% grade 3). Systolic blood pressure ≥160 mmHg occurred in 29% of patients, and 21% had diastolic blood pressure ≥100 mmHg. In unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), hypertension occurred in 45% of LENVIMA-treated patients (24% grade 3). Grade 4 hypertension was not reported in HCC.
Hypertension
Cardiac Dysfunction
Arterial Thromboembolic Events
Hepatotoxicity
Renal Failure or Impairment
Proteinuria
Diarrhea
Fistula Formation and Gastrointestinal Perforation
QT Interval Prolongation
Hypocalcemia
Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome (RPLS)
Hemorrhagic Events
Impairment of Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Suppression/Thyroid Dysfunction
Impaired Wound Healing
Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (ONJ)
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Adverse Reactions
Use in Specific Populations