Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma
KEYTRUDA, in combination with LENVIMA, is indicated for the first-line treatment of adult patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC).

KEYTRUDA, in combination with LENVIMA, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with advanced endometrial carcinoma that is mismatch repair proficient (pMMR) or not microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) as determined by an FDA-approved test, who have disease progression following prior systemic therapy in any setting and are not candidates for curative surgery or radiation.
PD-1 = programmed death receptor-1; TKI = tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Study Design and BASELINE Characteristics
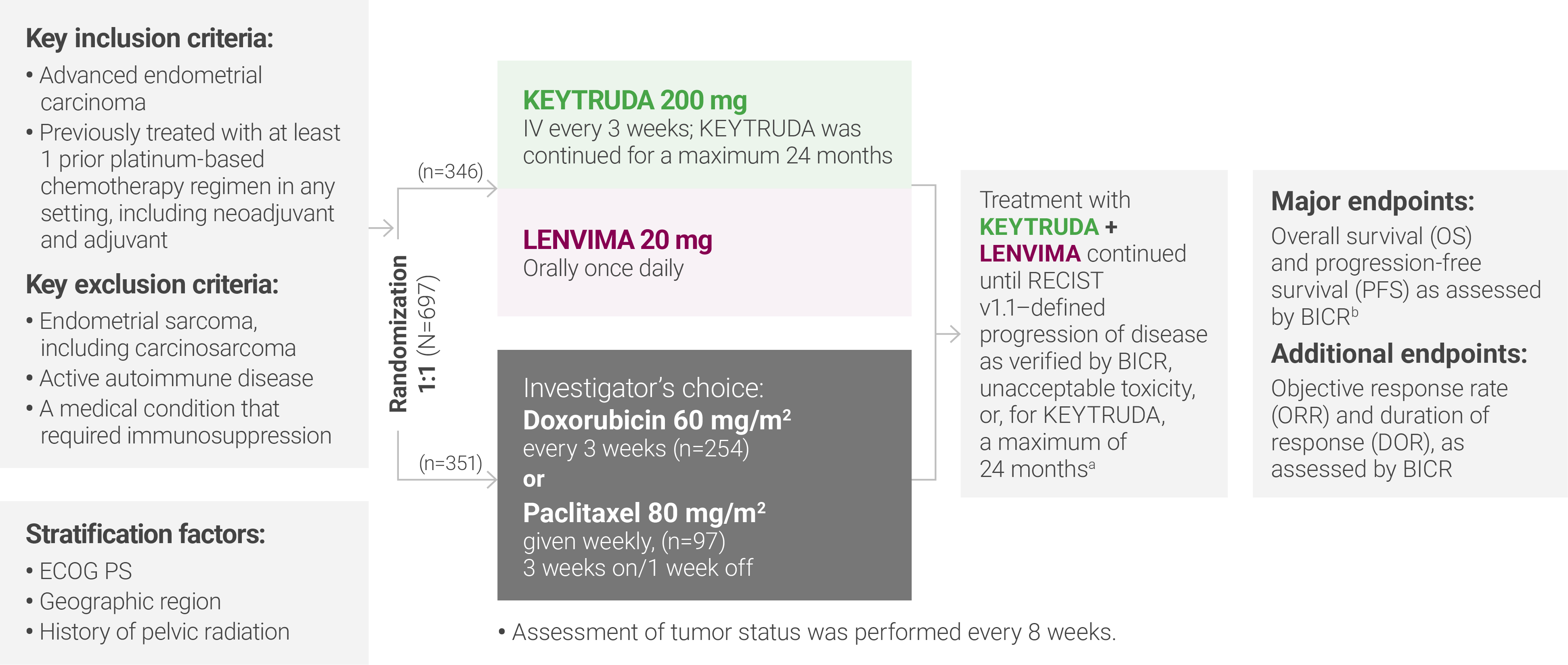
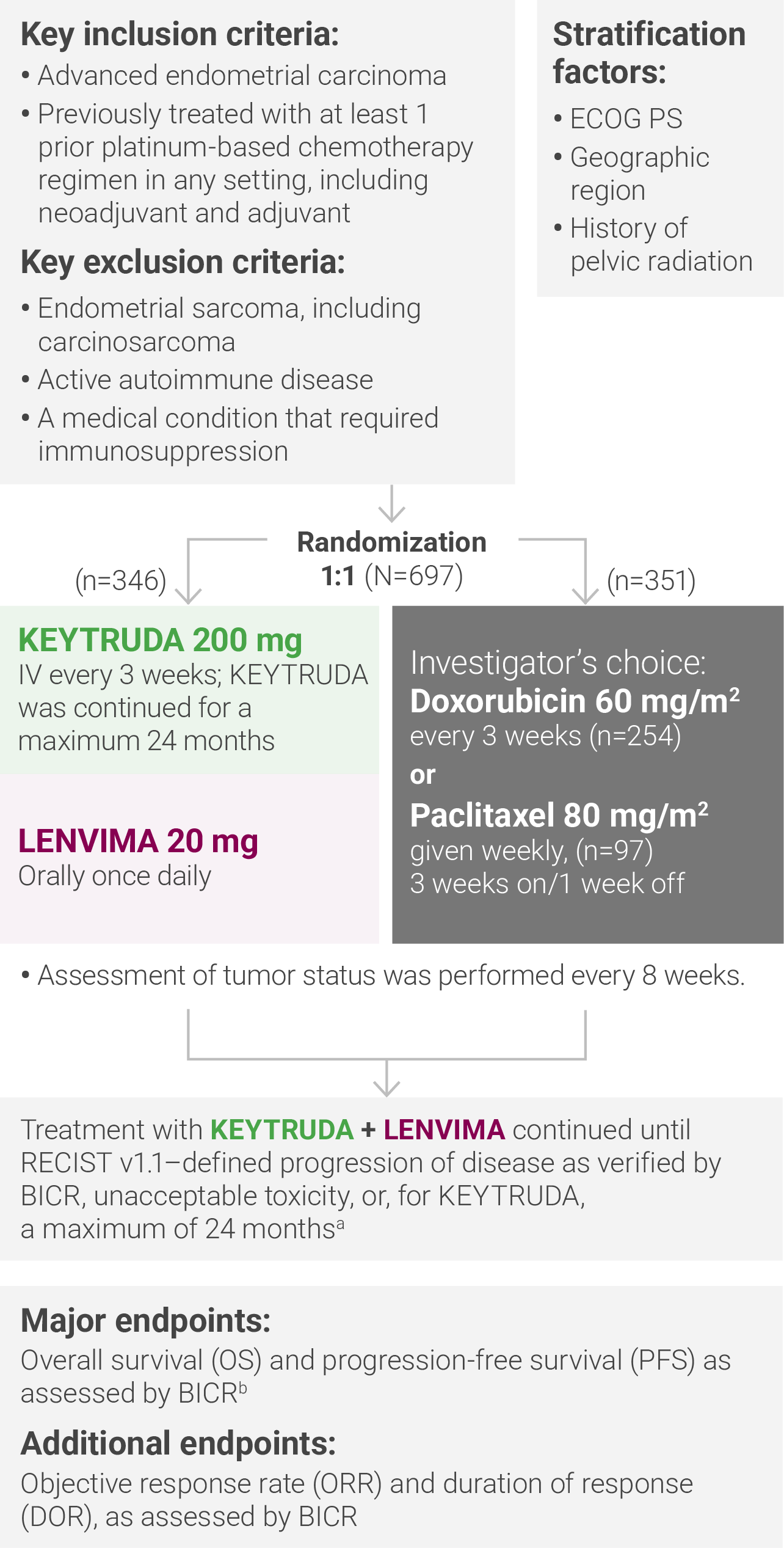
aTreatment was permitted beyond RECIST v1.1–defined disease progression if the treating investigator considered the patient to be deriving clinical benefit and the treatment was tolerated.
bAccording to RECIST v1.1, modified to follow a maximum of 10 target lesions and a maximum of 5 target lesions per organ.
ECOG PS = Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status; IV = intravenously; RECIST v1.1 = Response Evaluation Criteria In Solid Tumors v1.1; BICR = blinded independent central review.


HYPOTHETICAL PATIENTS
Patients experienced tumor recurrence/disease progression following prior systemic therapy, with no option for curative surgery or radiation.
Advanced endometrial carcinoma that is pMMR or not MSI-H as determined by an FDA-approved test
Disease progression following prior systemic therapy in any setting, including in the neoadjuvant and adjuvant settings
Not a candidate for curative surgery or radiation
Disease progression 11 months after receiving platinum-based regimen

Initial diagnosis:
Stage II endometrial carcinoma with grade 2 endometrioid histology
Biomarker status:
pMMR or not MSI-H,a determined at diagnosis
Surgery and radiation:
Total abdominal hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy with lymph node assessment, followed by EBRT
Disease recurrence:
At 18-month follow-up, PET/CT scan of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis revealed a tumor mass with invasion into the bladder and no evidence of lymph node involvement or distant metastases
First systemic therapy:
Platinum-based regimen
Disease progression:
11 months after completing 6 cycles of chemotherapy, CT revealed disease progression (liver metastases) with no option for curative surgery or radiation
aDetermined by an FDA-approved test.
BMI = body mass index; EBRT = external beam radiation therapy; PET = positron emission tomography; CT = computed tomography.
Disease recurrence 10 months after receiving adjuvant treatment

Initial diagnosis:
Stage IIIC1 endometrial carcinoma with grade 3 endometrioid histology
Biomarker status:
pMMR or not MSI-Ha
Surgery:
Total abdominal hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy and pelvic lymph node dissection
First systemic therapy and radiation:
Adjuvant treatment with carboplatin/paclitaxel and EBRT
Disease recurrence:
10 months after completing 6 cycles of chemotherapy, CT revealed her cancer had metastasized to her lungs, with no option for curative surgery or radiation
aDetermined by an FDA-approved test.
EBRT = external beam radiation therapy; CT = computed tomography.
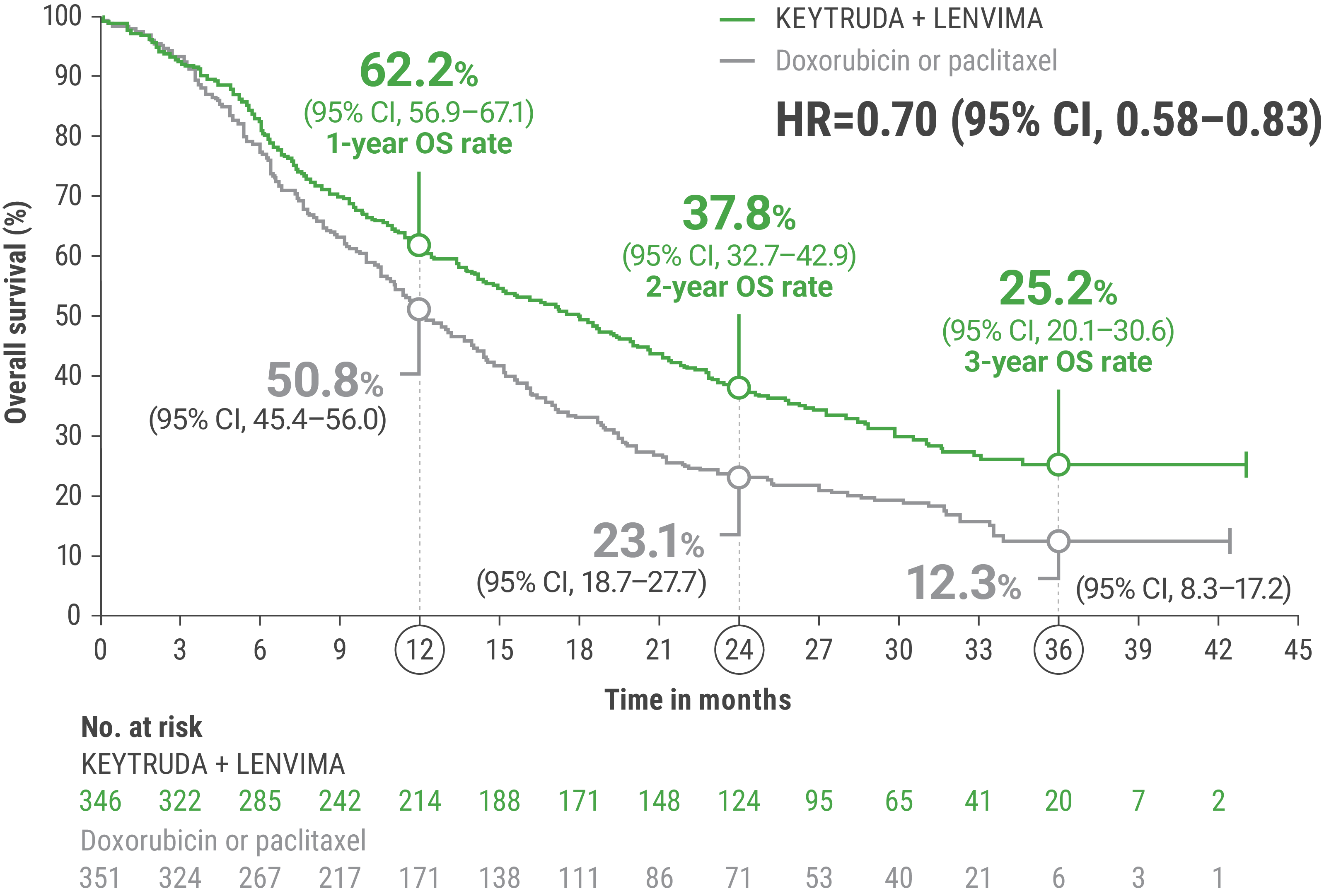
EFFICACY
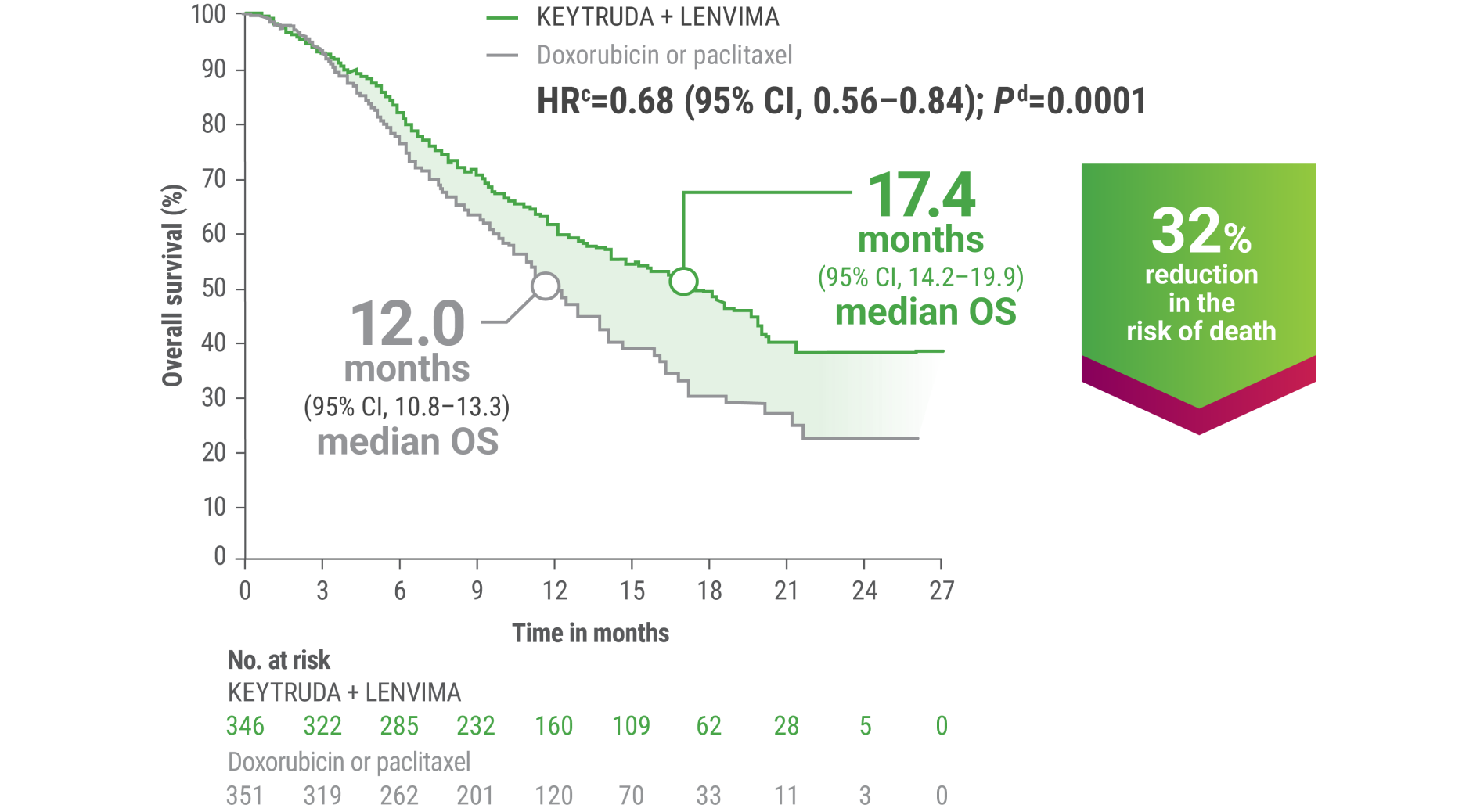
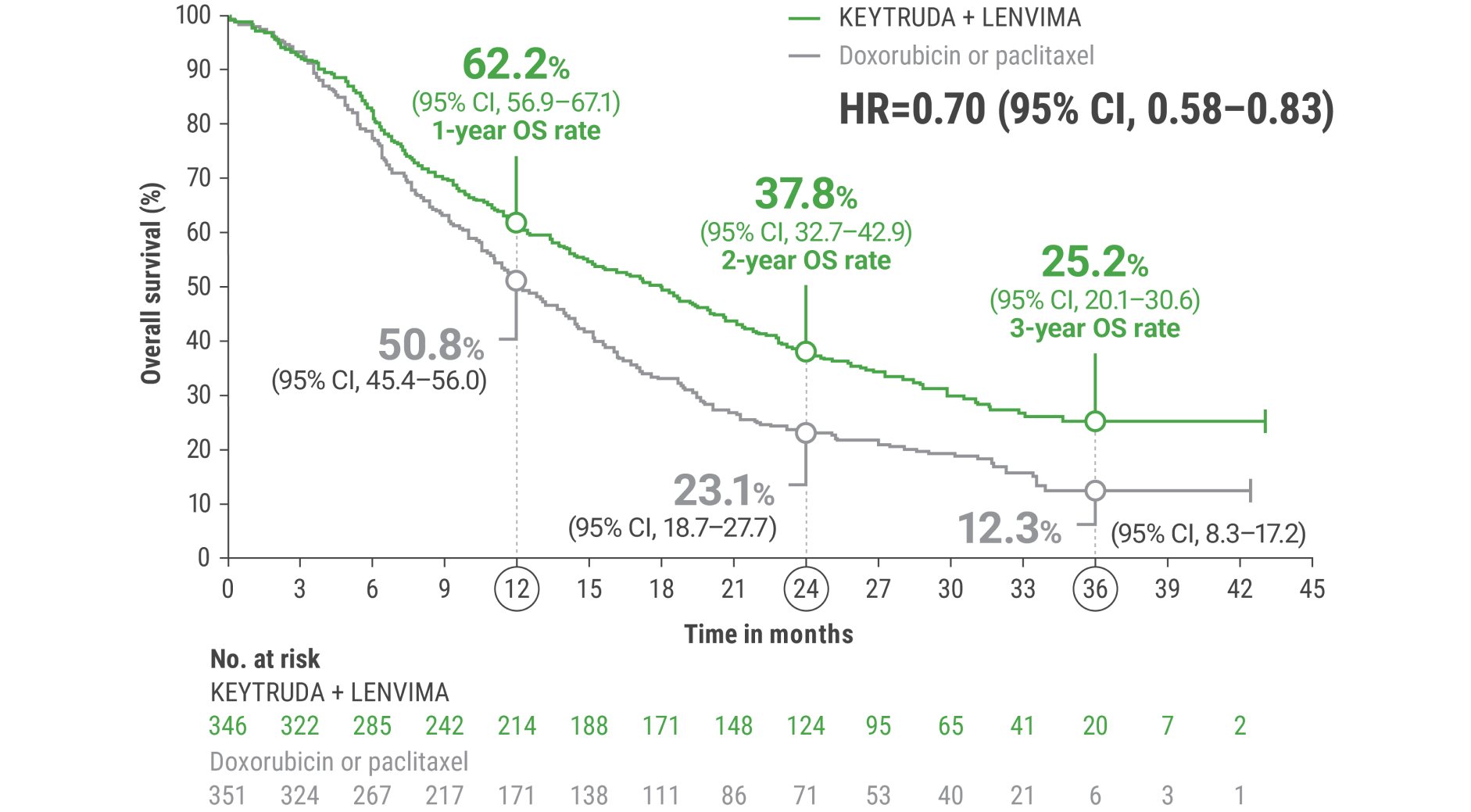
cBased on the stratified Cox regression model.
dBased on stratified log-rank test.
OS = overall survival; PFS = progression-free survival; ORR = objective response rate; HR = hazard ratio; CI = confidence interval.
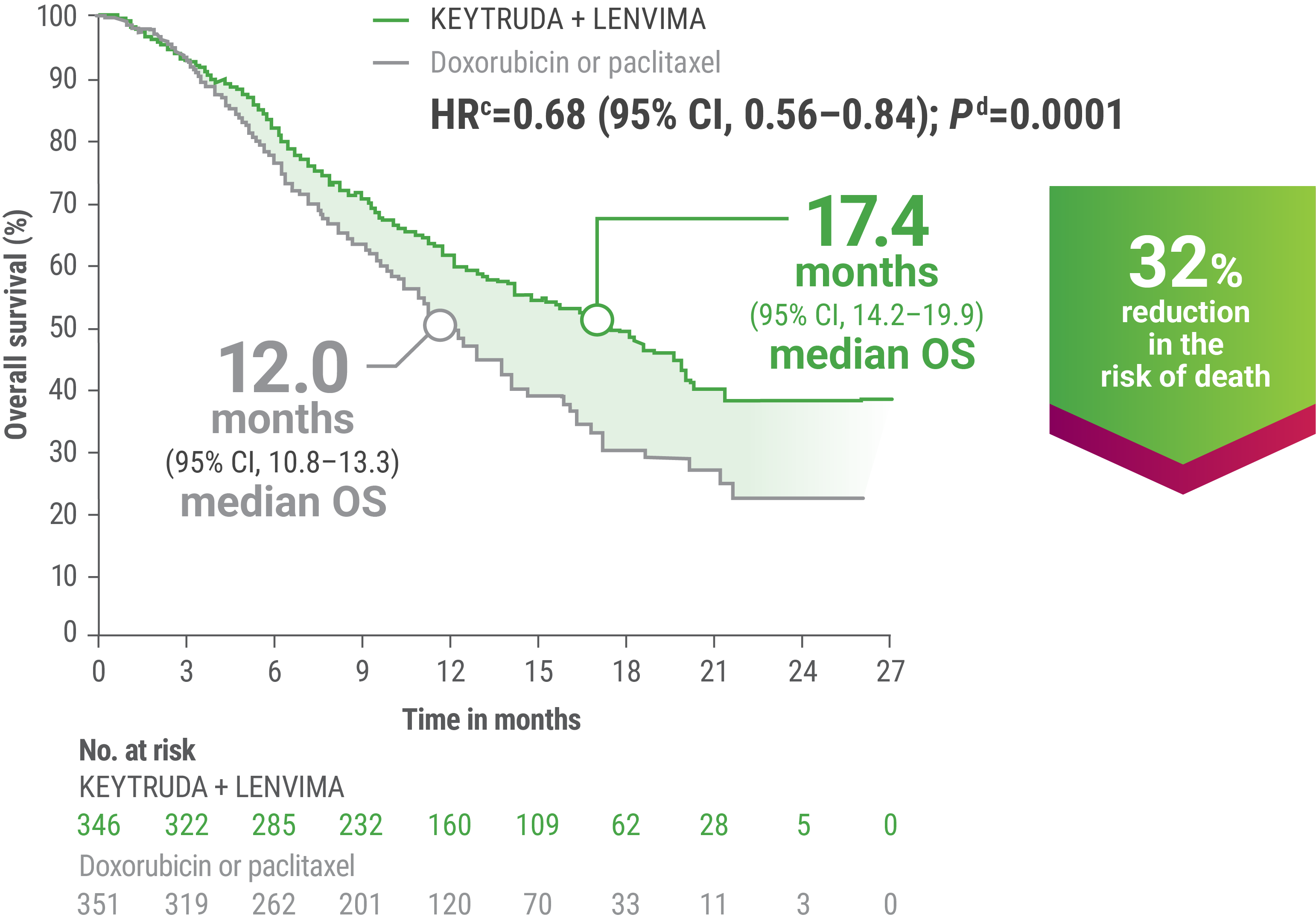
cBased on the stratified Cox regression model.
dBased on stratified log-rank test.
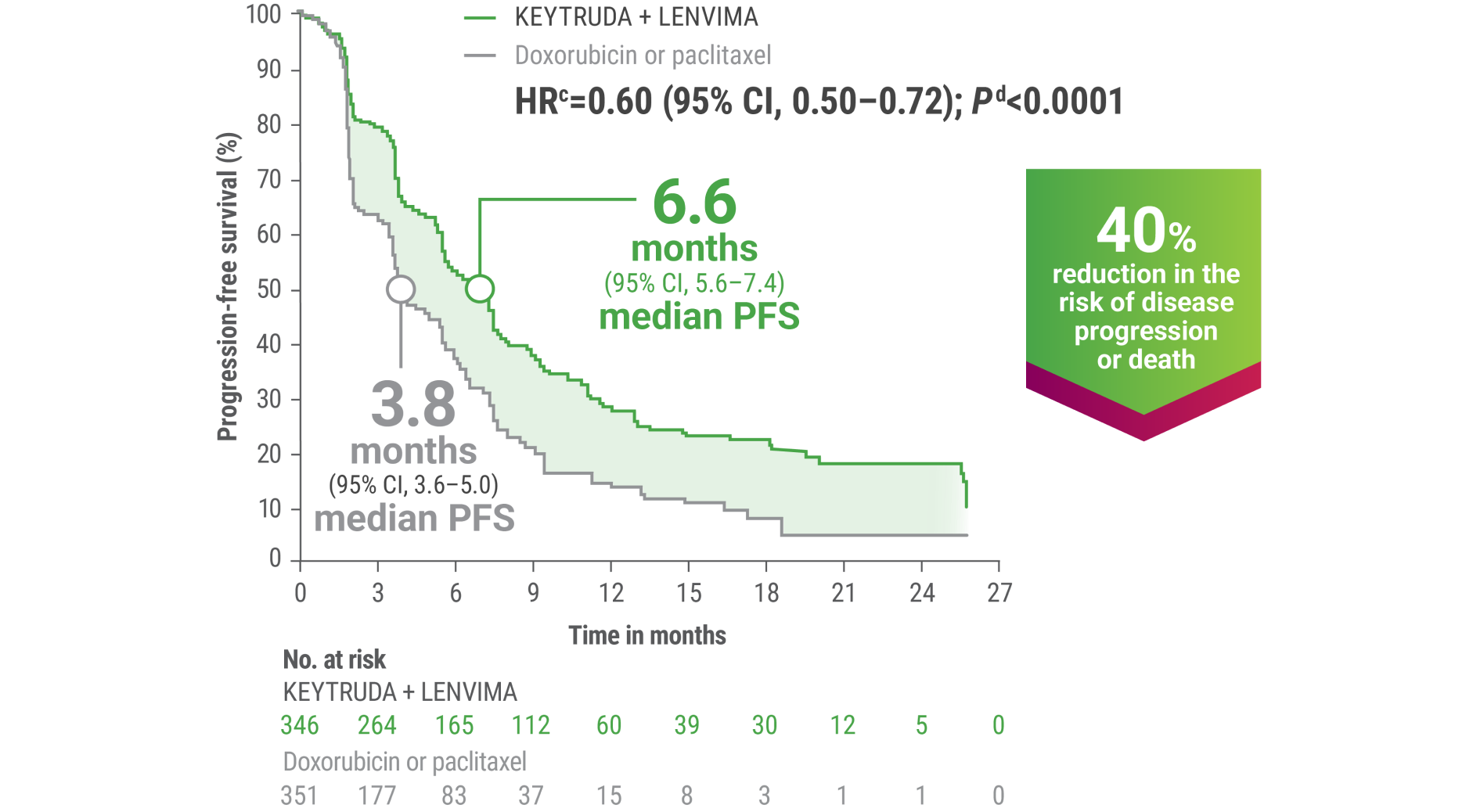
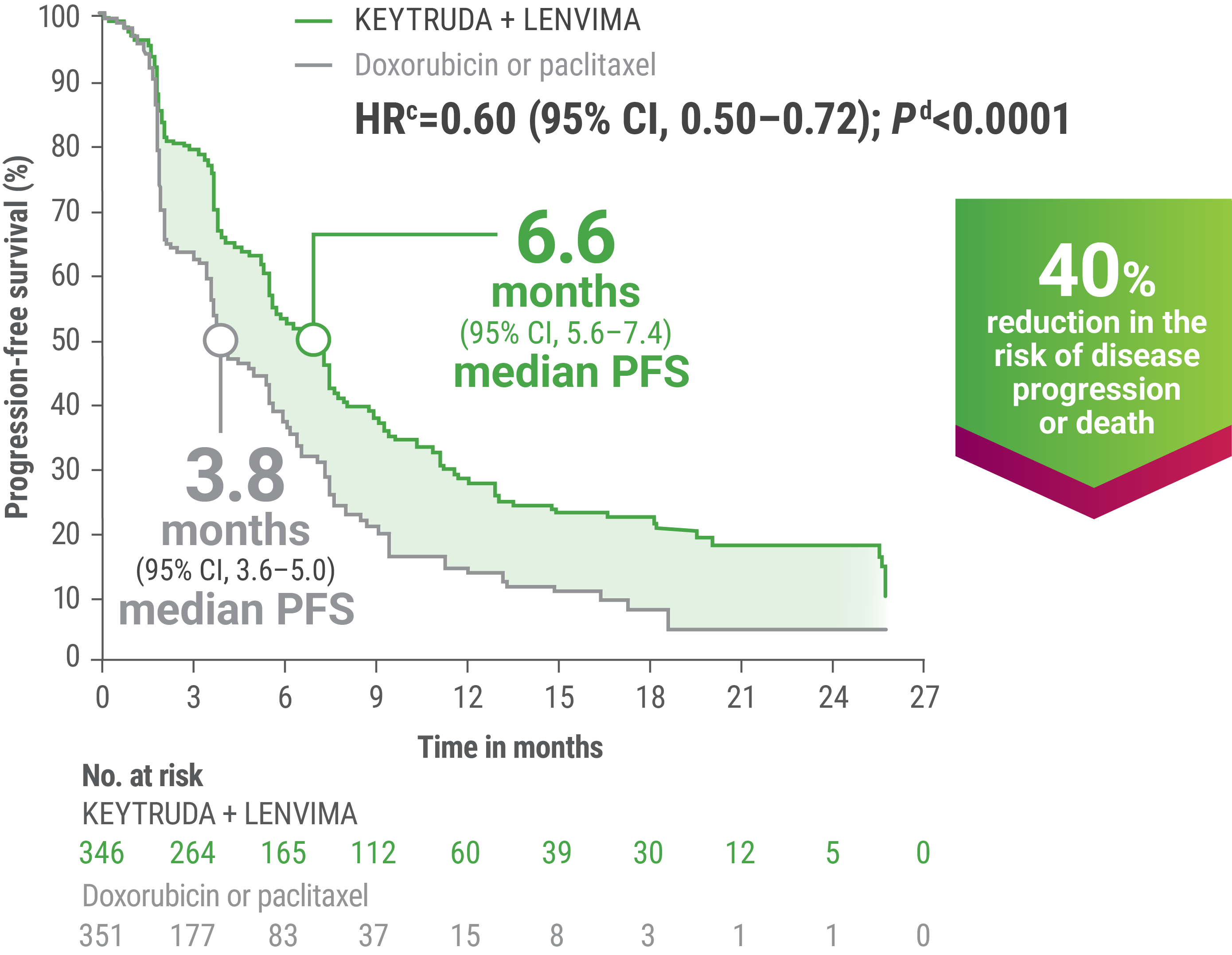
cBased on the stratified Cox regression model.
dBased on the stratified log-rank test.
ePer independent radiology review.
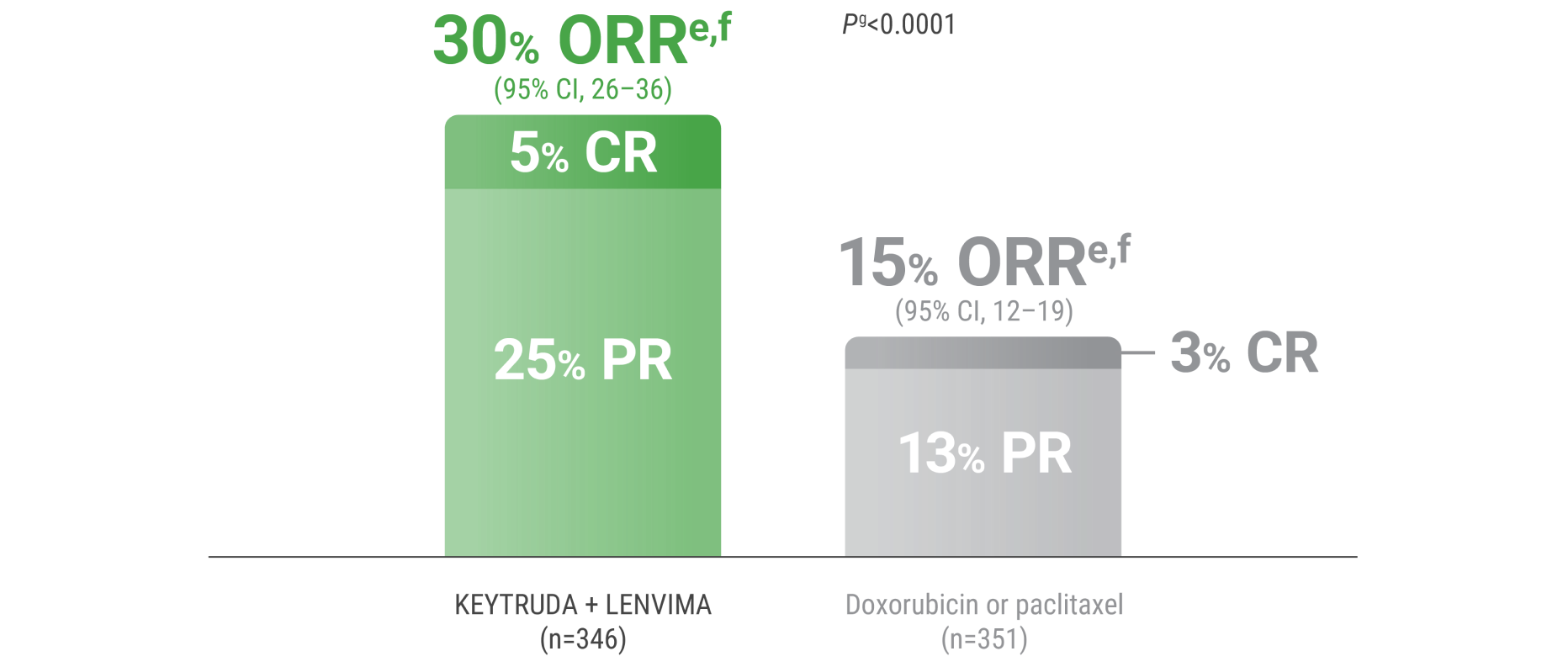
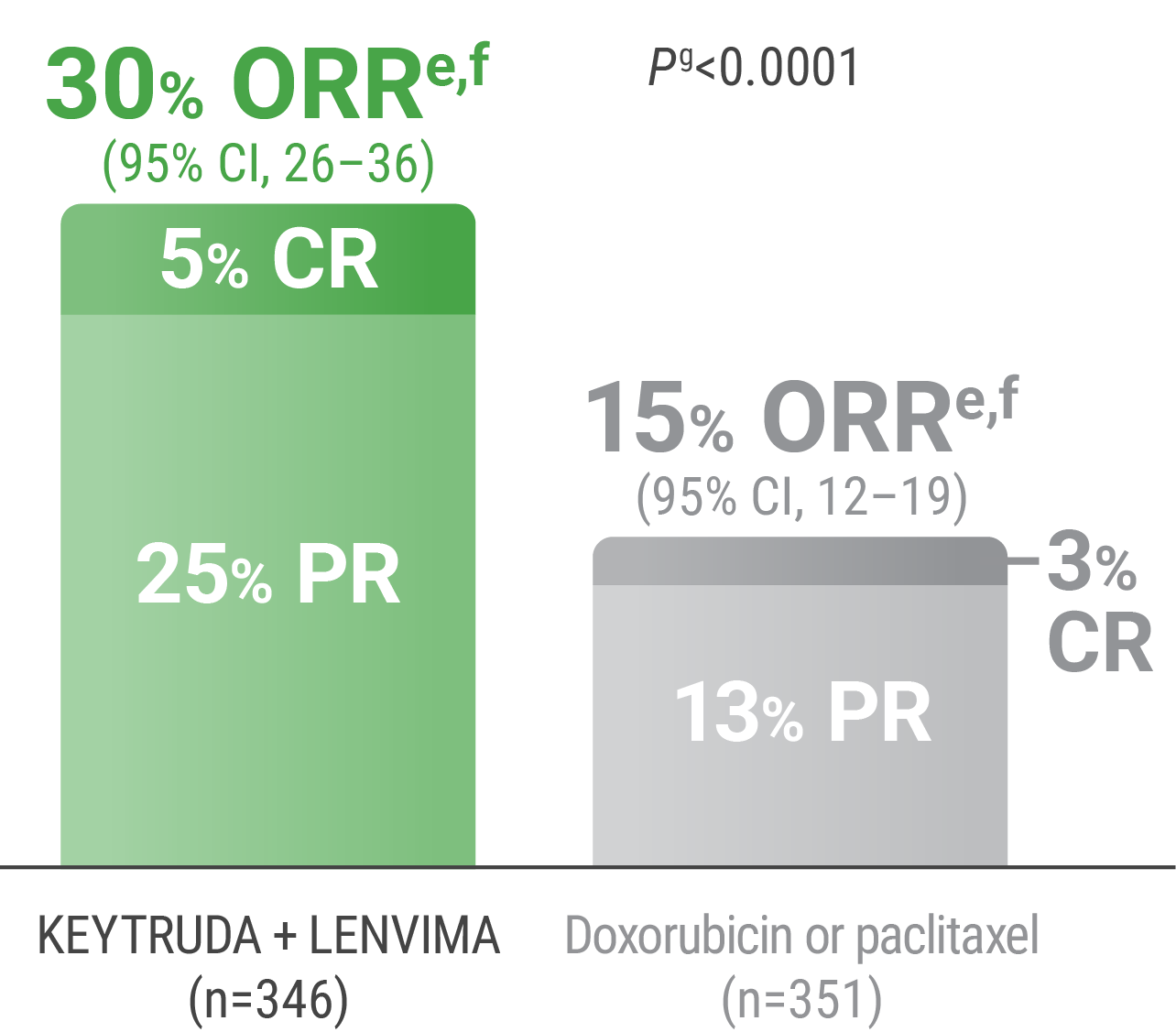
ePer independent radiology review.
fResponse: Best objective response as confirmed CR or PR.
gBased on Miettinen and Nurminen method stratified by ECOG PS, geographic region, and history of pelvic radiation.
CR = complete response; PR = partial response.
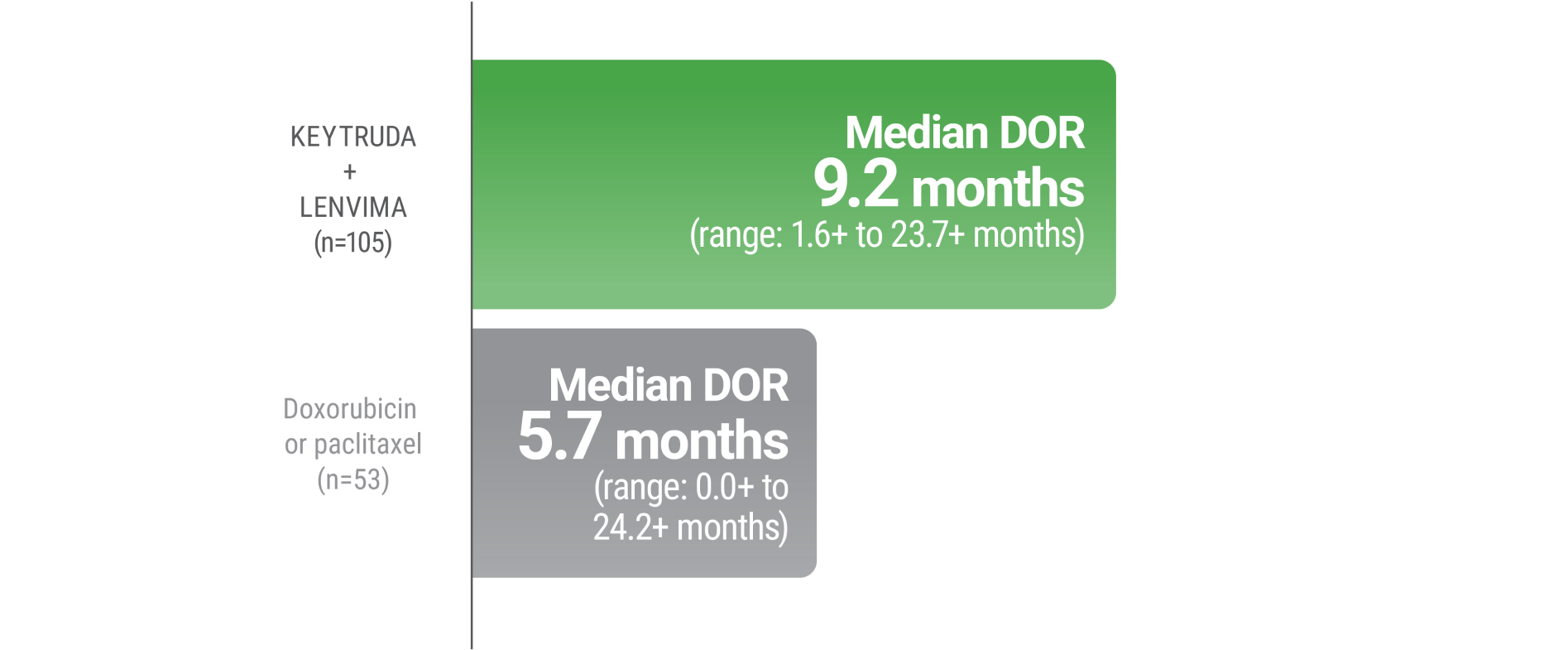
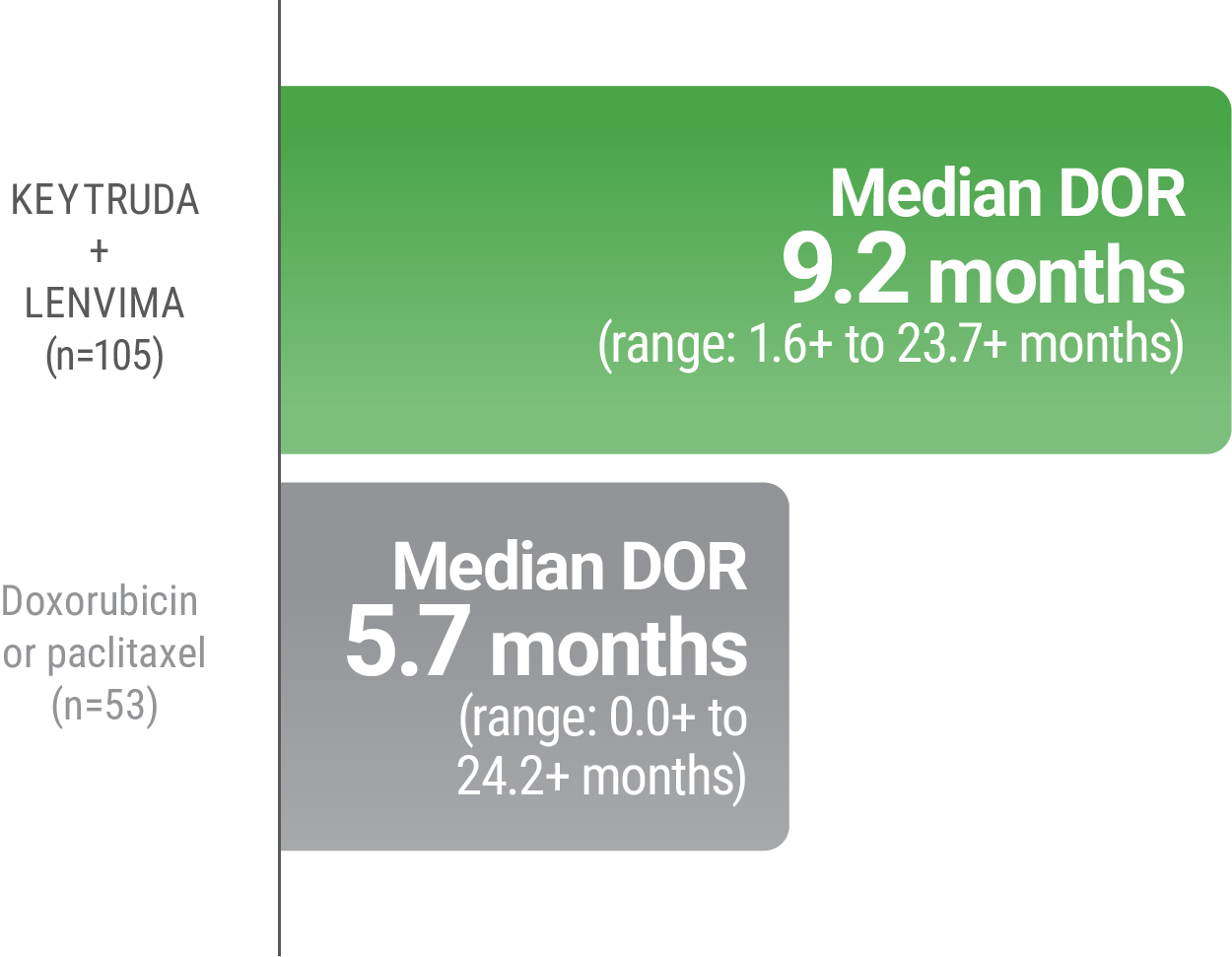
LIMITATION: No formal statistical testing was planned for the protocol-specified final OS analysis and, therefore, no conclusions can be drawn.10
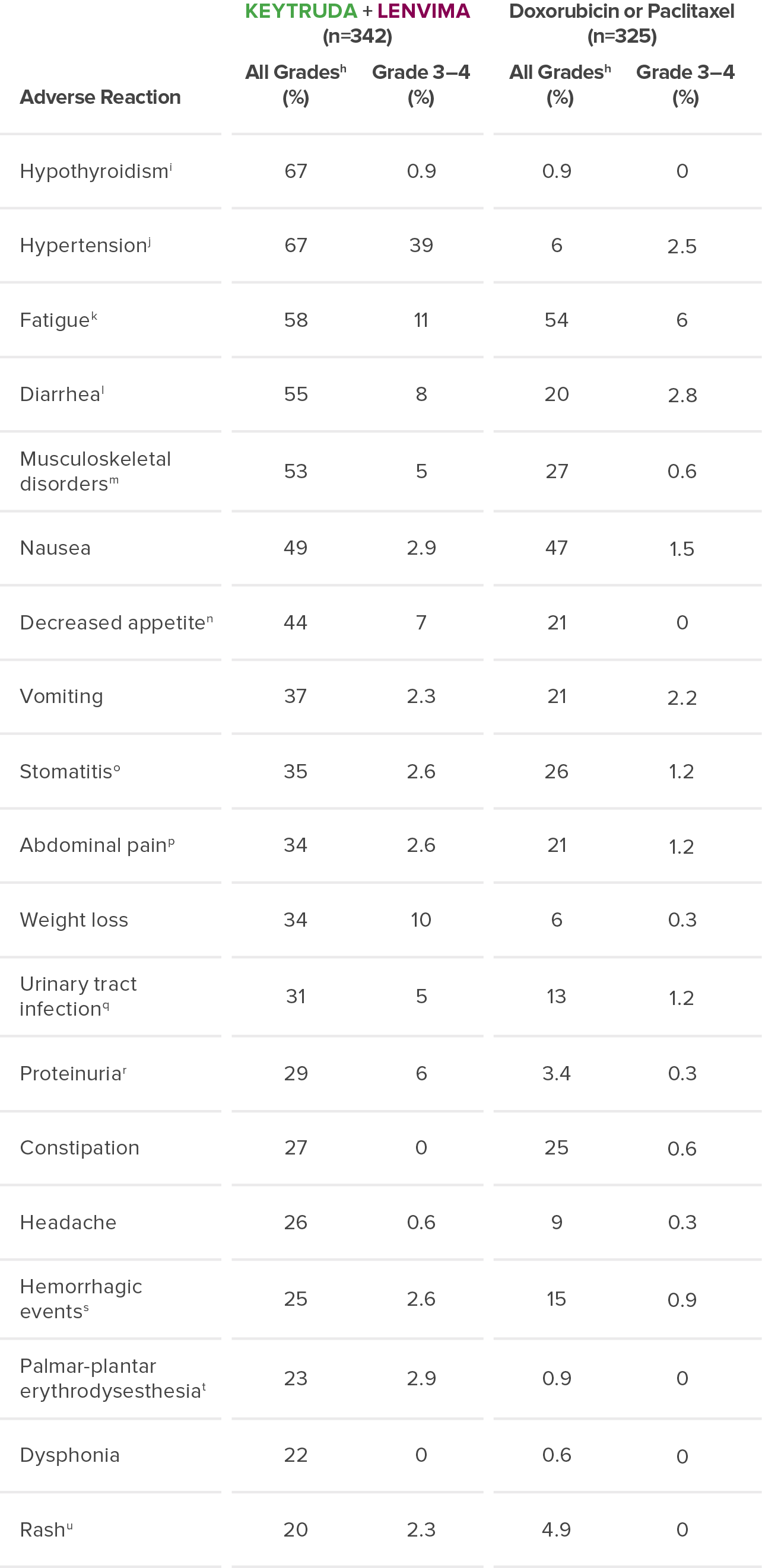
Adverse Reactions
The safety of KEYTRUDA + LENVIMA was investigated in KEYNOTE-775/Study 309 in patients treated with KEYTRUDA + LENVIMA (n=342) compared to doxorubicin or paclitaxel (n=325) at the protocol-specified interim analysis.7
Median duration of exposure (months)
6.8 (range: 1 day–25.8 months)
6.7 (range: 1 day–26.8 months)
Median duration of exposure (months)
6.8 (range: 1 day–25.8 months)
6.7 (range: 1 day–26.8 months)
Acute kidney injury
Acute myocardial infarction
Colitis
Decreased appetite
Intestinal perforation
Lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage
Malignant gastrointestinal obstruction
Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome
Myelodysplastic syndrome
Pulmonary embolism
Right ventricular dysfunction
Hypertension (4.4%)
Urinary tract infection (3.2%)
Discontinuation
15%
26%
Dose reduction
N/A
67%
Dose interruption
48%
58%
No dose reduction for
Hypertension (2%)
Asthenia (1.8%)
Diarrhea (1.2%)
Decreased appetite (1.2%)
Proteinuria (1.2%)
Vomiting (1.2%)
Diarrhea (8%)
Increased alanine aminotransferase (4.4%)
Increased aspartate aminotransferase (3.8%)
Hypertension (3.5%)
Hypertension (11%)
Diarrhea (11%)
Proteinuria (6%)
Decreased appetite (5%)
Vomiting (5%)
Increased alanine aminotransferase (3.5%)
Fatigue (3.5%)
Nausea (3.5%)
Abdominal pain (2.9%)
Weight decreased (2.6%)
Urinary tract infection (2.6%)
Increased aspartate aminotransferase (2.3%)
Asthenia (2.3%)
Palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia (2%)
Hypertension (18%)
Diarrhea (11%)
Palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome (9%)
Proteinuria (7%)
Fatigue (7%)
Decreased appetite (6%)
Asthenia (5%)
Weight decreased (5%)
No dose reduction for
Adverse Reaction
All Gradesh (%)
Grade 3–4 (%)
Doxorubicin or Paclitaxel (n=325)
All Gradesh (%)
Grade 3–4 (%)
Hypothyroidismi
67
0.9
0.9
0
Hypertensionj
67
39
6
2.5
Fatiguek
58
11
54
6
Diarrheal
55
8
20
2.8
Musculoskeletal disordersm
53
5
27
0.6
Nausea
49
2.9
47
1.5
Decreased appetiten
44
7
21
0
Vomiting
37
2.3
21
2.2
Stomatitiso
35
2.6
26
1.2
Abdominal painp
34
2.6
21
1.2
Weight loss
34
10
6
0.3
Urinary tract infectionq
31
5
13
1.2
Proteinuriar
29
6
3.4
0.3
Constipation
27
0
25
0.6
Headache
26
0.6
9
0.3
Hemorrhagic eventss
25
2.6
15
0.9
Palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesiat
23
2.9
0.9
0
Dysphonia
22
0
0.6
0
Rashu
20
2.3
4.9
0
hGraded per NCI-CTCAE v4.03.
iIncludes hypothyroidism, blood thyroid stimulating hormone increased, thyroiditis, primary hypothyroidism, secondary hypothyroidism.
jIncludes hypertension, blood pressure increased, hypertensive crisis, secondary hypertension, blood pressure abnormal, hypertensive encephalopathy, blood pressure fluctuation.
kIncludes fatigue, asthenia, malaise, lethargy.
lIncludes diarrhea, gastroenteritis.
mIncludes arthralgia, myalgia, back pain, pain in extremity, bone pain, neck pain, musculoskeletal pain, arthritis, musculoskeletal chest pain, musculoskeletal stiffness, non-cardiac chest pain, pain in jaw.
nIncludes decreased appetite, early satiety.
oIncludes stomatitis, mucosal inflammation, oropharyngeal pain, aphthous ulcer, mouth ulceration, cheilitis, oral mucosal erythema, tongue ulceration.
pIncludes abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, abdominal pain lower, abdominal discomfort, gastrointestinal pain, abdominal tenderness, epigastric discomfort.
qIncludes urinary tract infection, cystitis, pyelonephritis.
rIncludes proteinuria, protein urine present, hemoglobinuria.
sIncludes epistaxis, vaginal hemorrhage, hematuria, gingival bleeding, metrorrhagia, rectal hemorrhage, contusion, hematochezia, cerebral hemorrhage, conjunctival hemorrhage, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, hemoptysis, hemorrhage urinary tract, lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage, mouth hemorrhage, petechiae, uterine hemorrhage, anal hemorrhage, blood blister, eye hemorrhage, hematoma, hemorrhage intracranial, hemorrhagic stroke, injection site hemorrhage, melena, purpura, stoma site hemorrhage, upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage, wound hemorrhage, blood urine present, coital bleeding, ecchymosis, hematemesis, hemorrhage subcutaneous, hepatic hematoma, injection site bruising, intestinal hemorrhage, laryngeal hemorrhage, pulmonary hemorrhage, subdural hematoma, umbilical hemorrhage, vessel puncture site bruise.
tIncludes palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome, palmar erythema, plantar erythema, skin reaction.
uIncludes rash, rash maculo-papular, rash pruritic, rash erythematous, rash macular, rash pustular, rash papular, rash vesicular, application site rash.
NCI-CTCAE = National Cancer Institute-Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events.
hGraded per NCI-CTCAE v4.03.
iIncludes hypothyroidism, blood thyroid stimulating hormone increased, thyroiditis, primary hypothyroidism, secondary hypothyroidism.
jIncludes hypertension, blood pressure increased, hypertensive crisis, secondary hypertension, blood pressure abnormal, hypertensive encephalopathy, blood pressure fluctuation.
kIncludes fatigue, asthenia, malaise, lethargy.
lIncludes diarrhea, gastroenteritis.
mIncludes arthralgia, myalgia, back pain, pain in extremity, bone pain, neck pain, musculoskeletal pain, arthritis, musculoskeletal chest pain, musculoskeletal stiffness, non-cardiac chest pain, pain in jaw.
nIncludes decreased appetite, early satiety.
oIncludes stomatitis, mucosal inflammation, oropharyngeal pain, aphthous ulcer, mouth ulceration, cheilitis, oral mucosal erythema, tongue ulceration.
pIncludes abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, abdominal pain lower, abdominal discomfort, gastrointestinal pain, abdominal tenderness, epigastric discomfort.
qIncludes urinary tract infection, cystitis, pyelonephritis.
rIncludes proteinuria, protein urine present, hemoglobinuria.
sIncludes epistaxis, vaginal hemorrhage, hematuria, gingival bleeding, metrorrhagia, rectal hemorrhage, contusion, hematochezia, cerebral hemorrhage, conjunctival hemorrhage, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, hemoptysis, hemorrhage urinary tract, lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage, mouth hemorrhage, petechiae, uterine hemorrhage, anal hemorrhage, blood blister, eye hemorrhage, hematoma, hemorrhage intracranial, hemorrhagic stroke, injection site hemorrhage, melena, purpura, stoma site hemorrhage, upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage, wound hemorrhage, blood urine present, coital bleeding, ecchymosis, hematemesis, hemorrhage subcutaneous, hepatic hematoma, injection site bruising, intestinal hemorrhage, laryngeal hemorrhage, pulmonary hemorrhage, subdural hematoma, umbilical hemorrhage, vessel puncture site bruise.
tIncludes palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome, palmar erythema, plantar erythema, skin reaction.
uIncludes rash, rash maculo-papular, rash pruritic, rash erythematous, rash macular, rash pustular, rash papular, rash vesicular, application site rash.
NCI-CTCAE = National Cancer Institute-Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events.
NCCN RECOMMENDATION
NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) recommend pembrolizumab (
NCCN makes no warranties of any kind whatsoever regarding their content, use, or application and disclaims any responsibility for their application or use in any way.
vCategory 1 = Based upon high-level evidence (≥1 randomized phase 3 trials or high-quality, robust meta-analyses), there is uniform NCCN consensus (≥85% support of the Panel) that the intervention is appropriate.12
Useful in certain circumstances = Other interventions that may be used for selected patient populations (defined with recommendation).12
NCCN = National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®).
Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma
KEYTRUDA, in combination with LENVIMA, is indicated for the first-line treatment of adult patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
Advanced Endometrial Carcinoma
KEYTRUDA, in combination with LENVIMA, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with advanced endometrial carcinoma that is mismatch repair proficient (pMMR) or not microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) as determined by an FDA-approved test, who have disease progression following prior systemic therapy in any setting and are not candidates for curative surgery or radiation.
Severe and Fatal Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions
Immune-Mediated Pneumonitis
Immune-Mediated Colitis
Hepatotoxicity and Immune-Mediated Hepatitis
KEYTRUDA as a Single Agent
Immune-Mediated Endocrinopathies
Adrenal Insufficiency
Hypophysitis
Thyroid Disorders
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (DM), Which Can Present With Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Immune-Mediated Nephritis With Renal Dysfunction
Immune-Mediated Dermatologic Adverse Reactions
Other Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions
Infusion-Related Reactions
Complications of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (HSCT)
Increased Mortality in Patients With Multiple Myeloma
Embryofetal Toxicity
Adverse Reactions
Lactation
Hypertension
Cardiac Dysfunction
Arterial Thromboembolic Events
Hepatotoxicity
Renal Failure or Impairment
Proteinuria
Diarrhea
Fistula Formation and Gastrointestinal Perforation
QT Interval Prolongation
Hypocalcemia
Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome (RPLS)
Hemorrhagic Events
Impairment of Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Suppression/Thyroid Dysfunction
Impaired Wound Healing
Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (ONJ)
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Adverse Reactions
Use in Specific Populations
KEYTRUDA, in combination with LENVIMA, is indicated for the first-line treatment of adult patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
KEYTRUDA, in combination with LENVIMA, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with advanced endometrial carcinoma that is mismatch repair proficient (pMMR) or not microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) as determined by an FDA-approved test, who have disease progression following prior systemic therapy in any setting and are not candidates for curative surgery or radiation.
Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma
KEYTRUDA, in combination with LENVIMA, is indicated for the first-line treatment of adult patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
Advanced Endometrial Carcinoma
KEYTRUDA, in combination with LENVIMA, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with advanced endometrial carcinoma that is mismatch repair proficient (pMMR) or not microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) as determined by an FDA-approved test, who have disease progression following prior systemic therapy in any setting and are not candidates for curative surgery or radiation.
Severe and Fatal Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions: KEYTRUDA is a monoclonal antibody that belongs to a class of drugs that bind to either the programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1) or the programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1), blocking the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway, thereby removing inhibition of the immune response, potentially breaking peripheral tolerance and inducing immune-mediated adverse reactions. Immune-mediated adverse reactions, which may be severe or fatal, can occur in any organ system or tissue, can affect more than one body system simultaneously, and can occur at any time after starting treatment or after discontinuation of treatment. Important immune-mediated adverse reactions listed here may not include all possible severe and fatal immune-mediated adverse reactions.
Hypertension: In differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC), hypertension occurred in 73% of patients on LENVIMA (44% grade 3-4). In advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC), hypertension occurred in 42% of patients on LENVIMA + everolimus (13% grade 3). Systolic blood pressure ≥160 mmHg occurred in 29% of patients, and 21% had diastolic blood pressure ≥100 mmHg. In unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), hypertension occurred in 45% of LENVIMA-treated patients (24% grade 3). Grade 4 hypertension was not reported in HCC.
Severe and Fatal Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions
Immune-Mediated Pneumonitis
Immune-Mediated Colitis
Hepatotoxicity and Immune-Mediated Hepatitis
KEYTRUDA as a Single Agent
Immune-Mediated Endocrinopathies
Adrenal Insufficiency
Hypophysitis
Thyroid Disorders
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (DM), Which Can Present With Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Immune-Mediated Nephritis With Renal Dysfunction
Immune-Mediated Dermatologic Adverse Reactions
Other Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions
Infusion-Related Reactions
Complications of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (HSCT)
Increased Mortality in Patients With Multiple Myeloma
Embryofetal Toxicity
Adverse Reactions
Lactation
Hypertension
Cardiac Dysfunction
Arterial Thromboembolic Events
Hepatotoxicity
Renal Failure or Impairment
Proteinuria
Diarrhea
Fistula Formation and Gastrointestinal Perforation
QT Interval Prolongation
Hypocalcemia
Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome (RPLS)
Hemorrhagic Events
Impairment of Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Suppression/Thyroid Dysfunction
Impaired Wound Healing
Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (ONJ)
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Adverse Reactions
Use in Specific Populations
Severe and Fatal Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions: KEYTRUDA is a monoclonal antibody that belongs to a class of drugs that bind to either the programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1) or the programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1), blocking the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway, thereby removing inhibition of the immune response, potentially breaking peripheral tolerance and inducing immune-mediated adverse reactions. Immune-mediated adverse reactions, which may be severe or fatal, can occur in any organ system or tissue, can affect more than one body system simultaneously, and can occur at any time after starting treatment or after discontinuation of treatment. Important immune-mediated adverse reactions listed here may not include all possible severe and fatal immune-mediated adverse reactions.
Severe and Fatal Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions
Immune-Mediated Pneumonitis
Immune-Mediated Colitis
Hepatotoxicity and Immune-Mediated Hepatitis
KEYTRUDA as a Single Agent
Immune-Mediated Endocrinopathies
Adrenal Insufficiency
Hypophysitis
Thyroid Disorders
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (DM), Which Can Present With Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Immune-Mediated Nephritis With Renal Dysfunction
Immune-Mediated Dermatologic Adverse Reactions
Other Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions
Infusion-Related Reactions
Complications of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (HSCT)
Increased Mortality in Patients With Multiple Myeloma
Embryofetal Toxicity
Adverse Reactions
Lactation
Hypertension: In differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC), hypertension occurred in 73% of patients on LENVIMA (44% grade 3-4). In advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC), hypertension occurred in 42% of patients on LENVIMA + everolimus (13% grade 3). Systolic blood pressure ≥160 mmHg occurred in 29% of patients, and 21% had diastolic blood pressure ≥100 mmHg. In unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), hypertension occurred in 45% of LENVIMA-treated patients (24% grade 3). Grade 4 hypertension was not reported in HCC.
Hypertension
Cardiac Dysfunction
Arterial Thromboembolic Events
Hepatotoxicity
Renal Failure or Impairment
Proteinuria
Diarrhea
Fistula Formation and Gastrointestinal Perforation
QT Interval Prolongation
Hypocalcemia
Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome (RPLS)
Hemorrhagic Events
Impairment of Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Suppression/Thyroid Dysfunction
Impaired Wound Healing
Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (ONJ)
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Adverse Reactions
Use in Specific Populations